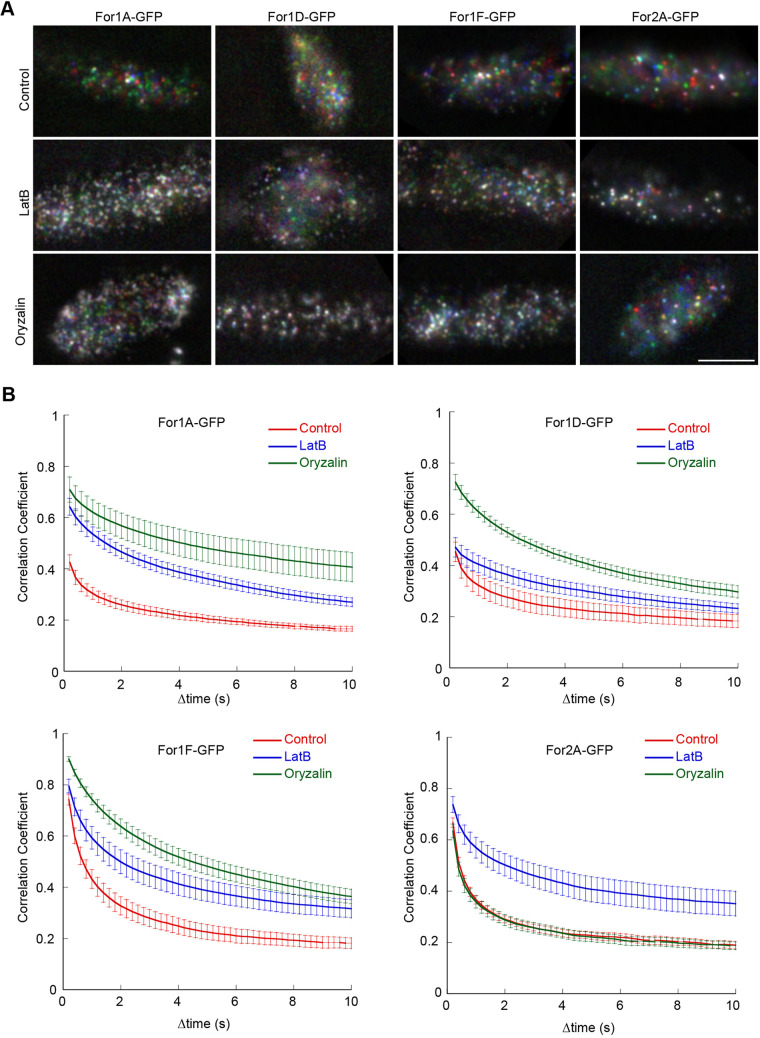
Fig. 7.
Formins are differentially affected by cytoskeletal inhibitors. (A) VAEM imaging of endogenously tagged formins at the cell cortex. See also Movie 11. Three frames taken every 200 ms from a time-lapse acquisition were false-colored red, green and blue and then merged into a single image. Movement of cortical dots from one frame to the next appear colored in the merge. If the particle does not move, then the red–green–blue merge results in a white particle. Scale bar: 2 µm. (B) Quantification of cortical formin dynamics under the indicated conditions. The correlation coefficient between two images was calculated at all possible temporal spacings (time interval). Error bars represent s.e.m. (n=10 cells except for For1A control, n=9; For1D LatB, n=8; For2A LatB, n=11).