Fig. 2.
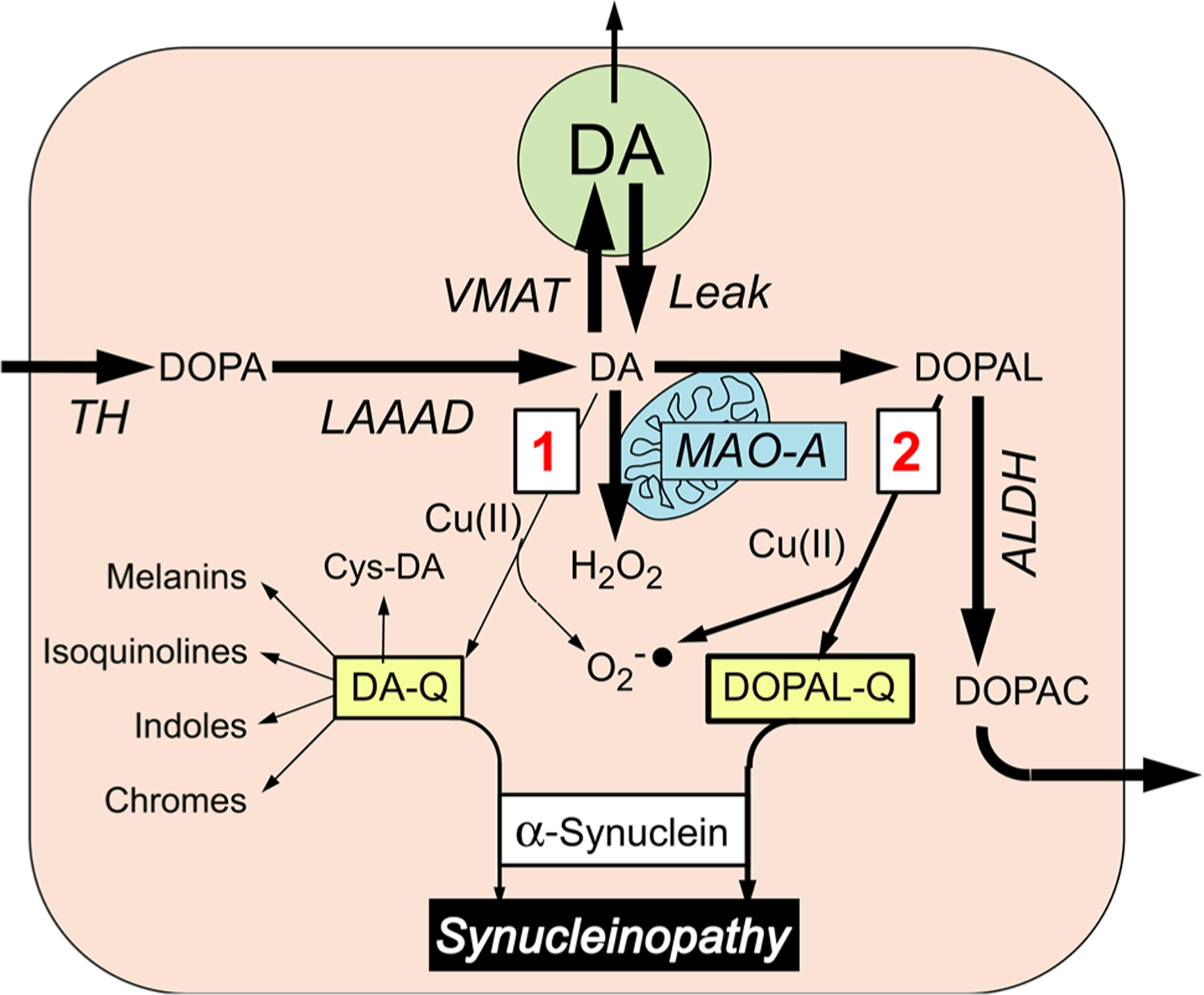
Alternative routes by which oxidation of cytoplasmic dopamine (DA) may modify alpha-synuclein. Most of cytoplasmic DA is taken up into vesicles via the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT); a minority undergoes oxidation, by two routes (red numbers in boxes). In route 1, DA is oxidized to form DA-quinone (DA-Q), with subsequent interactions with alpha-synuclein directly or via various further products of DA-Q, including 5-S-cysteinyldopamine (Cys-DA). In route 2, DA is oxidized enzymatically by monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A) in the outer mitochondrial membrane to form 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Cu(II) promotes the oxidation of DA and DOPAL. Formation of DA-Q and DOPAL-Q is associated with generation of superoxide radicals (). DOPAL is metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) to form 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), which exits the cell
