Fig. 3. Histopathological analysis of Slc1a4K/K brains.
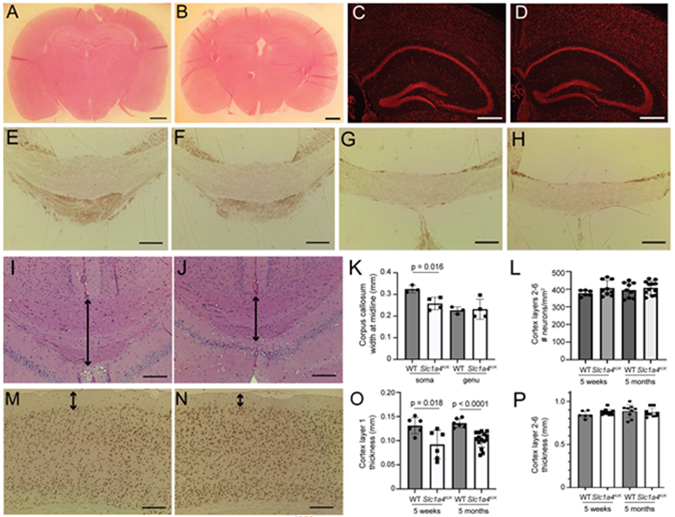
Coronal brain sections from wildtype (A,C,E,G,I,M) and Slc1a4K/K (B,D,F,H,J,N) mice were stained for hematoxylin and eosin (A,B,I,J), NeuroTrace (C,D), MBP (E-H), or NeuN (M-N) to assess morphology and myelination. Overall morphology appeared normal between wildtype and mutants (A-B), and there were no overt differences in the hippocampus or dentate gyrus (C,D). No differences in MBP staining were observed between wildtype and Slc1a4K/K mutants in the soma (E-F) or genu (G-H) of the corpus callosum. The soma of the corpus callosum, but not the genu, was significantly thinner in Slc1a4K/K mutant brains (arrows in I-J, quantified in K). No significant differences in number of neurons (L, quantified on NeuroTrace-stained sections) or thickness (P) were detected in cortex layers 2-6, but layer 1 was significantly thinner in Slc1a4K/K mutant brains at 5 weeks and 5 months of age (arrows in M-N, quantified in O). Scale bars: A-B = 10 mm; C-D = 500 μm; E-H,I,J,M,N = 200 μm. E,F,I,J = Bregma 1.7 mm, G-H = Bregma 0.5 mm.
