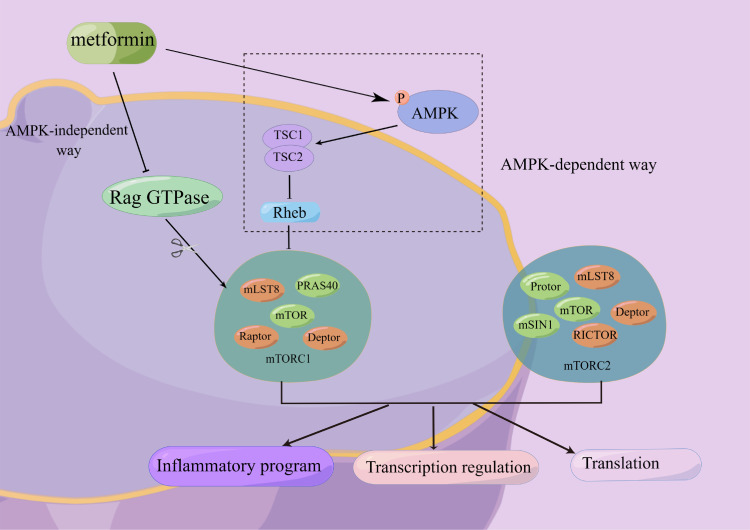
Figure 1.
Metformin inhibits mTOR both with and without activating AMPK. There are two ways that metformin could inhibit mTORC1 downstream: (1) After AMPK activity is activated, the TSC1/TSC2 complex (which can inhibit the activity of Rheb) is activated, and then the action of mTORC1 activity is inhibited. (2) Metformin inhibited Rag GTPase activity in an AMPK-independent manner, thereby inhibiting mTORC1. mTOR has two complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, which have important regulatory effects on inflammation, gene transcription, protein translation, etc.
Abbreviations: AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PRAS40, proline-rich Akt substrate 40; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex; RICTOR, rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR; Rheb, ras homolog enriched in the brain; mLST8, mammalian lethal with sec-13 protein 8; Raptor, regulatory associated protein of mTOR; Deptor, DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein; mSIN1, mammalian stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK)-interacting protein 1.