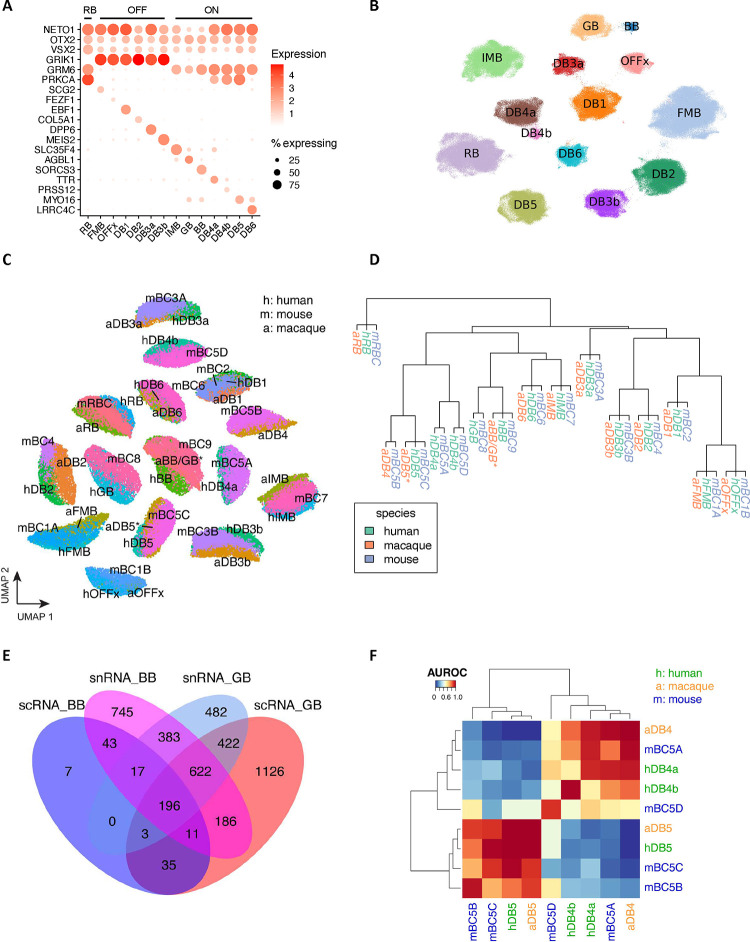
Figure 2. Bipolar cells.
A. Distribution of marker genes for BC types. BC subclasses are in RB, OFF and ON. NETO1, OTX2, and VSX2 were used as BC pan-markers. GRIK1 and GRM6 were used as OFF and ON markers, respectively. Rows represent marker genes, and columns represent BC types. The names of BC types are extracted from macaque BC types. B. UMAP visualization of human BC cells. Cell clusters are colored by the annotated cell types. C. Co-embedding of human, mouse, and macaque BC cells. To differentiate between cell types from three species, prefixes were added to the names: “h” for human, “m” for mouse, and “a” for macaque. D. Hierarchical clustering of mouse BC cell types. Expanded leaf nodes are the correspondent cell types from human and macaque BC cell types. E. The overlap between the top-ranked genes of human GB and BB is examined using snRNA-seq and scRNA-seq datasets. Fisher’s exact test was used to calculate the significance of the overlap of top ranked genes in GB (p-value=7.5×10−293) and BB (p-value=1.7×10−131) between snRNA-seq and scRNA-seq. F. Cell type similarities among mouse BC5A, BC5B, BC5C, and BC5D, and mapped types in humans and macaques.