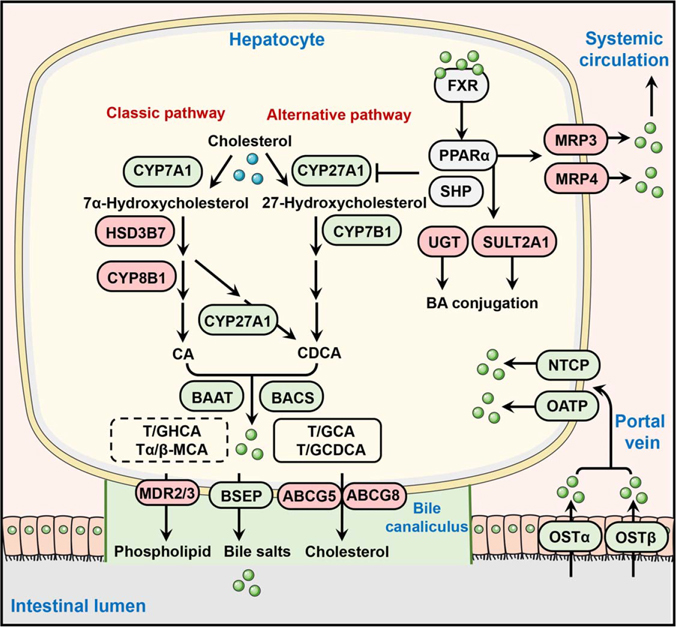
FIGURE 2.
Role of PPARα in the regulation of bile acid synthesis, transport, and metabolism. Bile acids activate the FXR-PPARα axis in hepatocytes to suppress bile acid synthesis primarily by inhibiting CYP7A1 (classic pathway) and CYP27A1 (alternative pathway). The activation of PPARα also promotes bile acid efflux from hepatocytes into the portal vein by induction of MRP3 and MRP4, and into bile canaliculus by induction of MDR2/MDR3 and ABCG5/ABCG8. In addition, PPARα activation represses bile acid reuptake into the liver by downregulating bile acid transporter OATP, NTCP, and OSTβ, as well as enhances the detoxification and metabolism of bile acids through the regulation of some target genes such as UGTs and SULT2A1. PPARα activation upregulates proteins. Filled green circles represent bile acids. Proteins upregulated by PPARα are shaded in red, and those downregulated by PPARα in green. Abbreviations: ABCG, ATP-binding cassette subfamily G; BAAT, bile acid-CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase; BACS, bile acid-CoA synthetase; BSEP, bile salt export pump; CA, cholic acid; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; CYP7A1, cytochrome P450 7A1; CYP7B1, cytochrome P450 7B1; CYP8B1, cytochrome P450 8B1; CYP27A1, cytochrome P450 27A1; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; HSD3B7, 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 7; MDR2/3, multidrug resistance protein 2/3; MRP, multidrug resistance-associated protein; NTCP, sodium/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; OATP, organic anion-transporting polypeptide; OSTα/β, organic solute transporter subunit α/β; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; SULT2A1, sulfotransferase 2A1; UGT, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase.