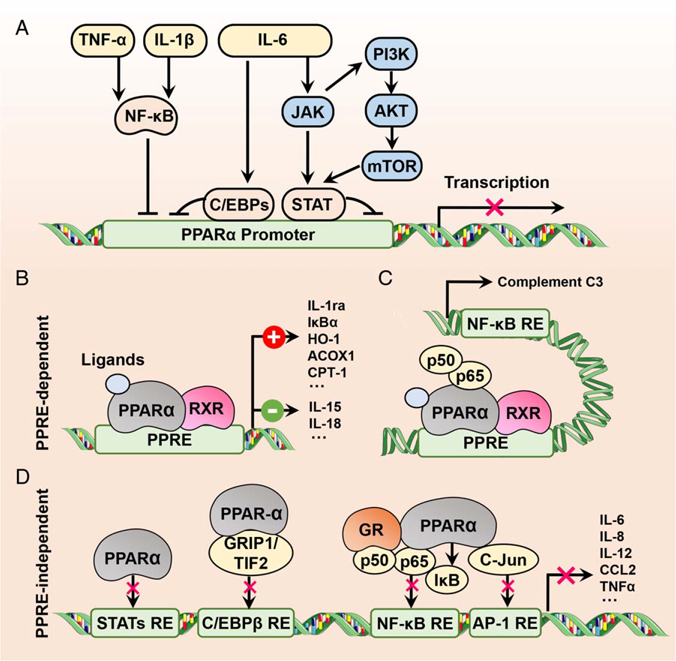
FIGURE 3.
Crosstalk between PPARα and inflammation. (A) Inflammatory cytokine-induced suppression of PPARα activity and/or expression using different proinflammatory transcription factors such as NF-κB, C/EBPs, and STATs. (B) PPARα activation-induced protection against inflammation through downregulating (−) proinflammatory cytokines or upregulating (+) anti-inflammatory factors in a PPRE-dependent manner. (C) Inhibition of NF-κB transcriptional activity by activated PPARα through PPRE-dependent abrogation of p65 binding to an NF-κB response element in the complement C3 promoter. (D) PPRE-independent inhibition of transrepression of proinflammatory cytokines. The transcriptional activity of proinflammatory transcription factors can be directly inhibited by PPARα or indirectly blocked by the interaction of PPARα with proteins. Abbreviations: ACOX1, acyl-CoA oxidase 1; AP-1, activator protein-1; C/EBPs, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein isoforms; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; CPT-1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; GRIP1, glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; IL-1ra, IL-1 receptor antagonist; IκBα, inhibitor of NF-κB alpha; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PPRE, PPAR-response element; RXR, retinoid X receptor; STATs, signal transduction and activator of transcription isoforms; TIF2, transcriptional intermediary factor 2.