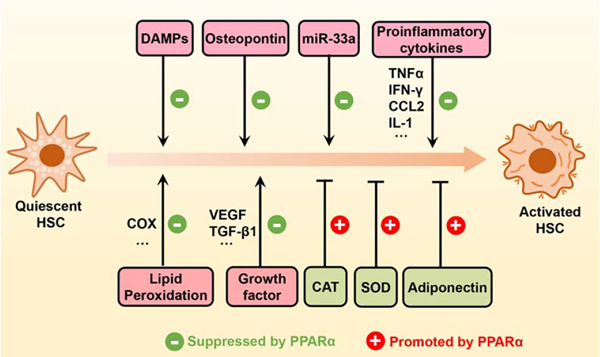
FIGURE 4.
PPARα activation indirectly suppresses HSC activation. Upon ligand activation, PPARα can inhibit HSC activation through different mechanisms, such as transcriptional upregulation of catalase, SOD1, and adiponectin, potentiation of the action of miR-33a, and direct or indirect inhibition of various profibrogenic mediators (DAMPs, osteopontin, etc.), proinflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IFN-γ, CCL2, IL-1, etc.), growth factors (VEGF, TGF-β1, etc.), and ROS. Abbreviations: CAT, catalase; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; COX, cyclooxygenase; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD1, superoxide dismutase 1.