Figure 8. Working model of DELLA-mediated transcriptional regulation.
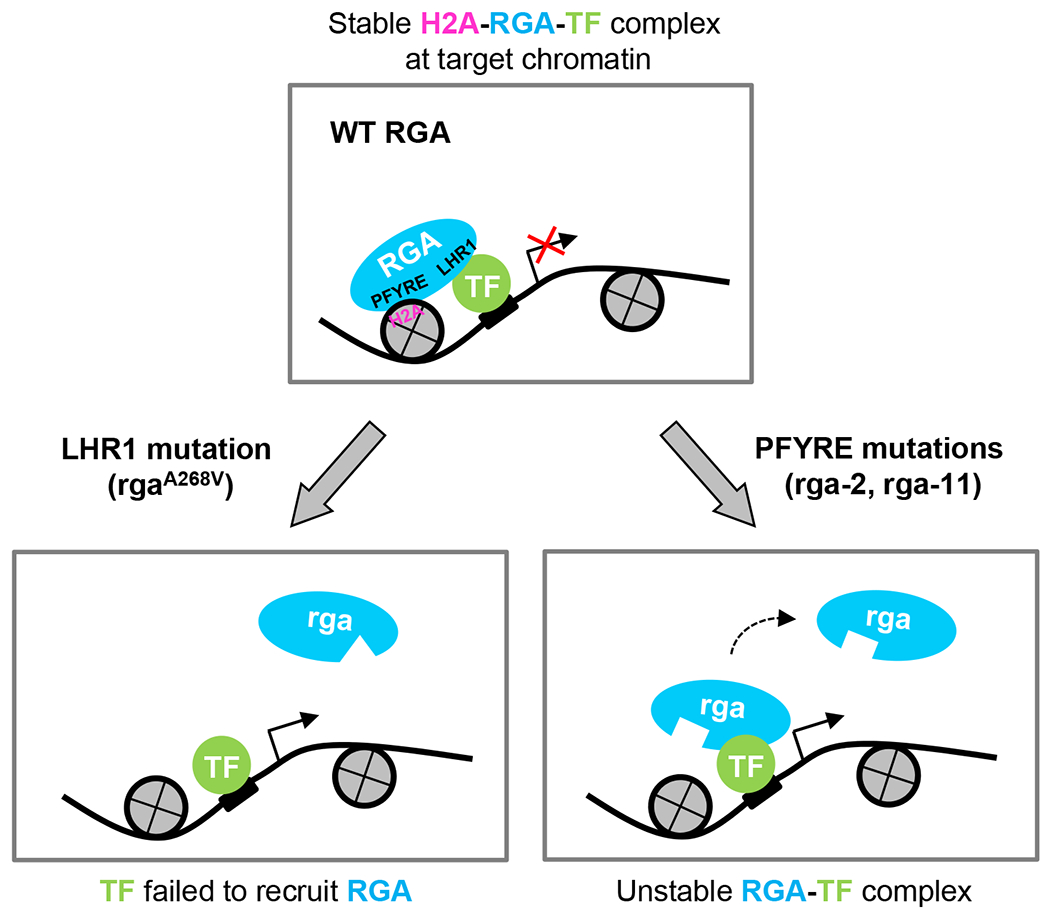
DELLA proteins (e.g., RGA) are recruited to target chromatin by interaction with TFs via the LHR1 subdomain. The transient TF-RGA interaction is stabilized by RGA-H2A binding (via its PFYRE subdomain) to form TF-RGA-H2A complexes at the target chromatin. Mutations in the LHR1 subdomain (e.g., rgaA268V) prevent recruitment to target chromatin by the TFs. In contrast, mutations in the PFYRE subdomain (e.g., rga-2 and rga-11) abolish H2A binding. Both subdomains are essential for DELLA-mediated transcription repression and activation. The diagram only depicts RGA-mediated transcription repression. A similar diagram can depict RGA-mediated transcription activation, except that the TF-RGA-H2A complex will promote transcription of target genes and that either LHR1 or PFYRE mutations will reduce transcription.
