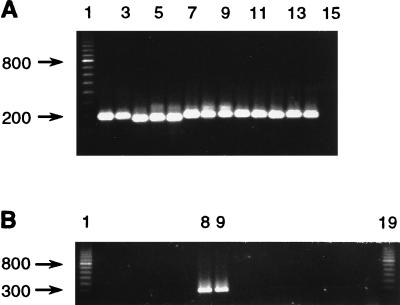
FIG. 5.
Amplification of DNA obtained by the Chelex method. (A) Amplification with primers 358f and 517r. Lane 2, Aeromonas salmonicida ATCC 33658; lane 3, Aeromonas sp.; lane 4, Carnobacterium piscicola ATCC 35586; lane 5, Corynebacterium striatum; lane 6, Cytophaga sp. strain DSM 3660 (Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen); lane 7, E. coli; lane 8, P. salmonis LF-89; lane 9, P. salmonis EM-90; lane 10, Pseudoalteromonas antarctica CECT 4664 (Colección Española de Cultivos Tipos); lane 11, Pseudoalteromonas atlantica ATCC 19262; lane 12, Renibacterium salmoninarum ATCC 33209; lane 13, Vibrio anguillarum ATCC 43305; lane 14, Yersinia ruckeri ATCC 29473; lane 15, extraction control. Lane 1 contained a 100-bp ladder. (B) Amplification with primers RTS1 and RTS4. In lanes 1 to 15, the order of DNAs and the initial DNA concentration in each PCR are the same as in panel A. Lanes 16 through 18 contained additional negative controls, and lane 19 contained a 100-bp ladder.