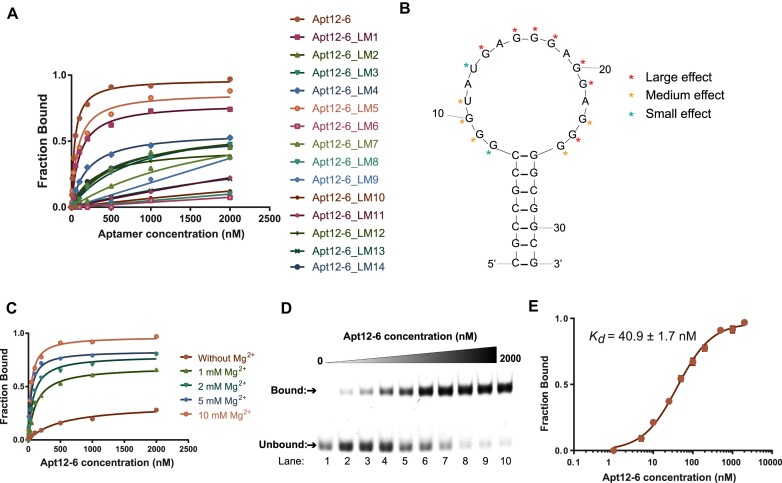
Figure 2.
Binding analysis reveals Apt12-6 binds strongly to L-c-kit 1 dG4 with nanomolar affinity. (A) Mutational analysis of Apt12-6. Fourteen loop mutant (LM) constructs were designed based on the principle of G to A, U to C and C to U single nucleotide substitution in the loop region. The binding results of them showed L-c-kit 1 binds strongest to Apt12-6. (B) Single nucleotide mutational analysis results of each LM construct based on binding curve from (A). (C) Optimization of Mg2+ concentration for in vitro binding analysis of Apt12-6 to L-c-kit 1. Kd(5 mM Mg2+) = 42.3 ± 5.5 nM. Kd(2 mM Mg2+) = 78.9 ± 8.1 nM. Kd(1 mM Mg2+) = 126.1 ± 18.1 nM. A concentration of 10 mM Mg2+ was selected for further investigation. (D) EMSA shows the binding between Apt12-6 and FAM-L-c-kit 1 dG4. With increasing concentration of Apt12-6 (lanes 1–10: 0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 2000 nM), the unbound band intensity decreases and the bound band intensity increases, indicating the interaction between Apt12-6 and FAM-L-c-kit 1 dG4. (E) Binding curve of FAM-L-c-kit 1 dG4 against Apt12-6 based on data from (D). The Kd is determined to be 40.9 ± 1.7 nM. The error bar represents the standard error of the mean (SEM) of three independent replicates.