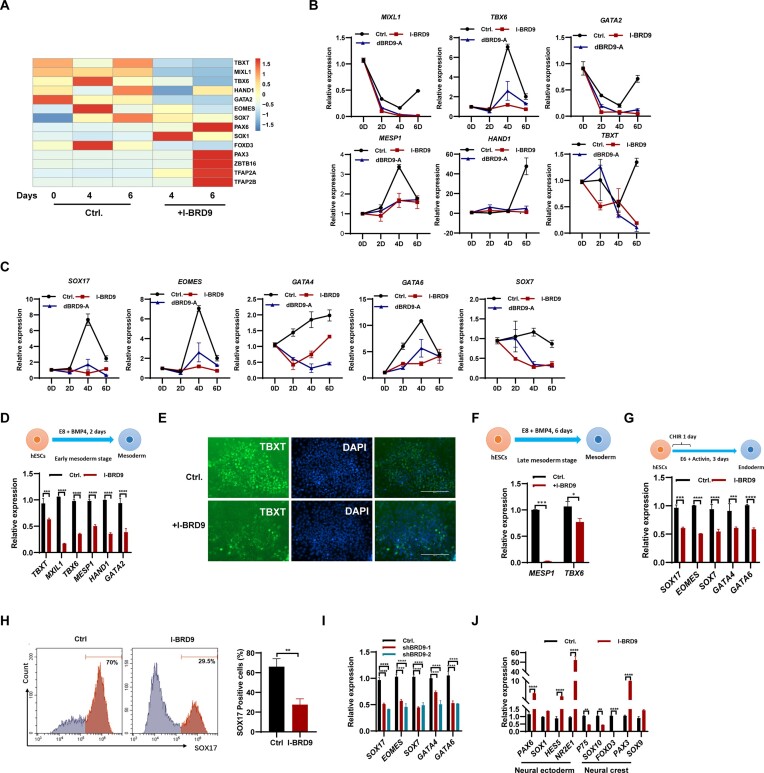
Figure 2.
Deficiency of BRD9 suppresses the differentiation of hESCs into meso-endoderm, while promoting their differentiation into neural ectoderm. (A) Heatmap displaying the expression of genes associated with three germ layers during spontaneous differentiation of H1 cells in E6 medium with I-BRD9 (10 μM) treatment on days 4 and 6. (B) qPCR analysis of transcript levels of mesoderm marker genes MIXL1, TBXT6, GATA2, MESP1, HAND1 and TBXT in H1 cells in E6 medium with 100 nM dBRD9-A treatment on days 2, 4 and 6. (C) qPCR analysis of transcript levels of endoderm marker genes SOX17, EOMES, GATA4, GATA6 and SOX7 in H1 cells in E6 medium with dBRD9-A treatment on days 2, 4 and 6. (D) qPCR analysis of transcript levels of mesoderm marker genes TBXT, MIXL1, TBXT6, MESP1, HAND1 and GATA2 in BMP4-induced early mesoderm differentiation of hESCs with and without 10 μM I-BRD9 treatment for 2 days. (E) Immunostaining of TBXT in BMP4-induced early mesoderm differentiated from hESCs treated or not with 10 μM I-BRD9 for 2 days. (F) qPCR analysis of MESP1 and TBX6 transcript levels in the BMP4-induced late mesoderm differentiation stage of hESCs treated or not with 10 μM I-BRD9 for 6 days. (G) Schematic of the endoderm differentiation of hESCs. qPCR analysis of transcript levels of endoderm markers SOX17, EOMES, SOX7, GATA4 and GATA6 in hESCs differentiated into endoderm with and without I-BRD9 treatment. (H) Flow cytometry analysis of SOX17 protein expression in control and 10 μM I-BRD9-treated hESCs under endoderm differentiation conditions. (I) qPCR analysis of SOX17, EOMES, SOX7, GATA4 and GATA6 transcript levels in endoderm differentiated from hESCs with BRD9 knocked down. (J) Transcript levels of neuroectoderm markers PAX6, SOX1, HES5 and NR2E1 and neural crest marker P75, SOX10, FOXD3, PAX3 and SOX9 in H1 cells cultured in E6 medium upon BRD9 inhibition with 10 μM I-BRD9 for 4 days.