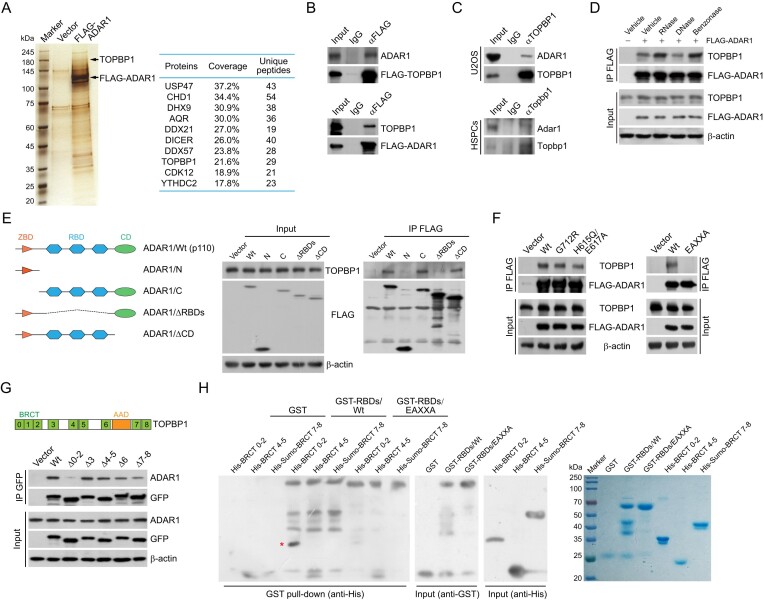
Figure 2.
ADAR1 is physically associated with TOPBP1. (A) Analysis of FLAG-ADAR1-associated proteins. Differential protein bands of the immunoprecipitates from HeLa cell extracts were retrieved from silver-stained SDS-PAGE, digested with trypsin, and analyzed by mass spectrometry. The parameters of the representatively top 10 candidates are shown. (B) Immunoprecipitation (IP) followed by immunoblotting (IB) with cellular extracts from HeLa cells expressing FLAG-TOPBP1 or FLAG-ADAR1. (C) Co-IP analysis of the interaction between TOPBP1 and ADAR1 with cellular extracts from U2OS cells and mouse HSPCs. (D) Co-IP analysis of the association of TOPBP1 with FLAG-ADAR1 in the absence or presence of different nucleases as indicated. (E, F) Co-IP analysis of the association of TOPBP1 with the indicated FLAG-tagged ADAR1 mutants in HeLa cells. A schematic of ADAR1 domains and its deletion mutants is shown in (E). (G) Co-IP analysis of the interaction of ADAR1 with GFP-tagged TOPBP1 deletion mutants. A schematic of TOPBP1 domains is shown. BRCT, BRCA1 C-terminal; AAD, ATR activation domain. (H) GST pull-down assays with recombinant ADAR1 RNA-binding domains (GST-RBDs/Wt or GST-RBDs/EAXXA) and TOPBP1 BRCT domains (His-BRCT 0–2, His-BRCT 4–5 and His-Sumo-BRCT 7–8). High salt and heparin column was used to remove contaminating RNAs for RBD purification. The recombinant proteins were examined by Coomassie brilliant blue staining and immunoblotting. The pulled-down protein is marked by a red asterisk.