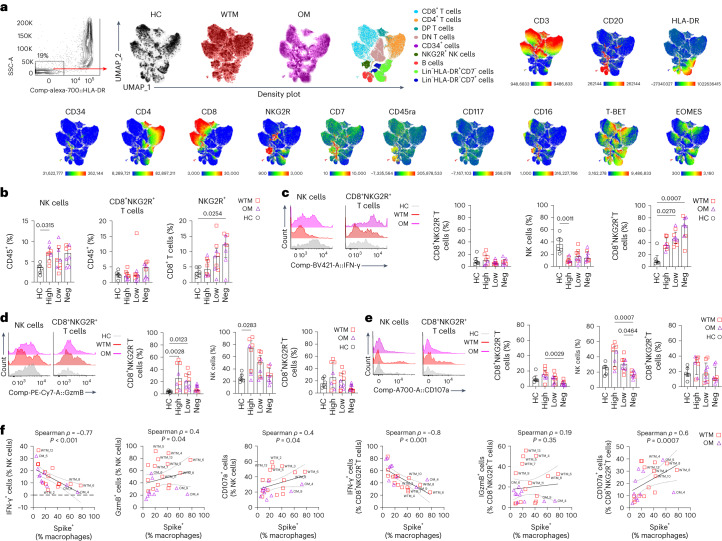
Fig. 4. Frequency of IFN-γ+ NKG2R+ cells negatively correlates with frequency of Spike+ Mac.
a, Unsupervised analysis by the UMAP dimension reduction algorithm of Singlet, live, CD45+CD14− lymphocytes isolated from BALF of WTM (n = 15), OM (n = 10) at >221 d p.i. and HC (n = 6). Cells were gated, downsampled to 3,000 cells per sample, barcoded and concatenated. CD45 was excluded from the list of UMAP running parameters. Density plot for each group of monkeys is shown. Manually gated lymphocyte populations shown on the UMAP plot with the corresponding color; intensities of each marker used in the analysis shown on the UMAP plots. b, Frequency of NKG2R+ lymphocyte in BALF cells of WTM, OM and HC at least 221 d p.i. c–e, Histograms (left) and frequency (right) of IFN-γ (c), granzyme B (d) and CD107a (e) in NKG2R− T cells, NKG2R+ NK cells and CD3+NKG2R+ T cells from the BALF of WTM, OM and HC as in a. f, Spearman correlation analysis of the frequencies of IFN-γ+, GzmB+, CD107a+ cells among NKG2R+ cells and frequencies of Spike+ Mac in BALF cells. In all graphs, the median and the interquartile range are shown. P values were determined using a Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test. In the correlation analyses, the black solid line represents linear regression, and the dotted lines represent the confidence interval (95%).