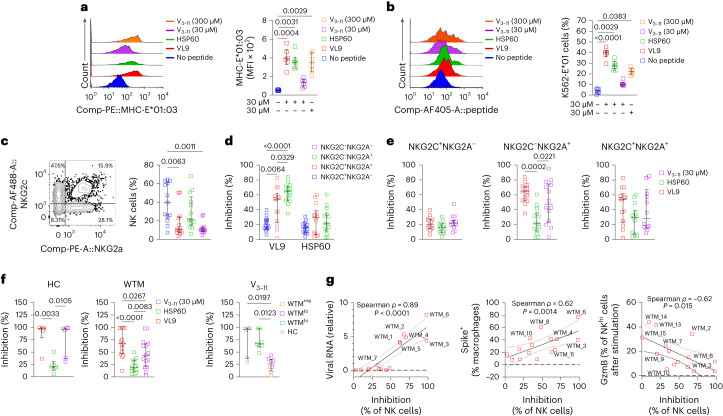
Fig. 8. Spike leader sequence peptide inhibits NK cell lysis.
a, Histogram showing the MFI of MHC-E in K562 cells transduced with MHC-E (MHC-E*01:03) after peptide loading (VL9, HSP60, V3–11) and culture for 12 h (left), and graph illustrating the expression of MHC-E in MHC-E*01:03 cells after peptide loading (with VL9, HSP60, and V3–11 peptides) compared to the control condition with no peptides, following a 12-h culture (right). b, Histogram displaying the MFI of biotinylated peptides (VL9, HSP60, V3–11) loaded into MHC-E*01 cells and revealed through conjugation with streptavidin, following a 12-h culture period (left) and expression of biotinylated peptides (VL9, HSP60, V3–11) in MHC-E*01:03 cells after peptide loading (with VL9, HSP60 and V3–11 peptides), in comparison to the control condition with no peptides, following a 12-h culture period (right). c, Dot plot illustrating the distribution of blood NK cells from 13 human PBMCs collected before 2019 based on NKG2A and NKG2C expression (left) and frequency of NKG2C+NKG2A−, NKG2C+NKG2A+ and NKG2C−NKG2A+ cell subsets in human PBMCs collected before 2019 (right). d, Inhibition of degranulation in human NKG2C+NKG2A−, NKG2C+NKG2A+, NKG2C−NKG2A+ and NKG2C−NKG2A− NK cell subsets exposed to K562-E-01 cells loaded with VL9 and HSP60 peptides during an 8-h coculture, as in c. e, Inhibition of degranulation in human NKG2C+NKG2A−, NKG2C−NKG2A+ and NKG2C+NKG2A+ NK subsets during 8-h coculture with VL9, HSP60 and the spike-derived peptide V3–11. f, Inhibition of degranulation in BALF NKG2R+ NK cells isolated ≥461 d p.i. from 15 WTM and incubated with V3–11 peptide-loaded K562-E-01 cells for 8 h. g, Spearman correlation analysis between V3–11 peptide-induced inhibition of NKG2R+ NK cell degranulation and viral load measured in Fig. 2a, Spike+ Mac frequency measured in Fig. 2c and GzmB expression in NKG2Rhi NK cells in total BALF cells of WTM after 24 h of spike stimulation, as measured in Fig. 7b. Each symbol represents an individual; bars represent medians. Interquartile ranges are shown. In all graphs, P values were determined by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test.