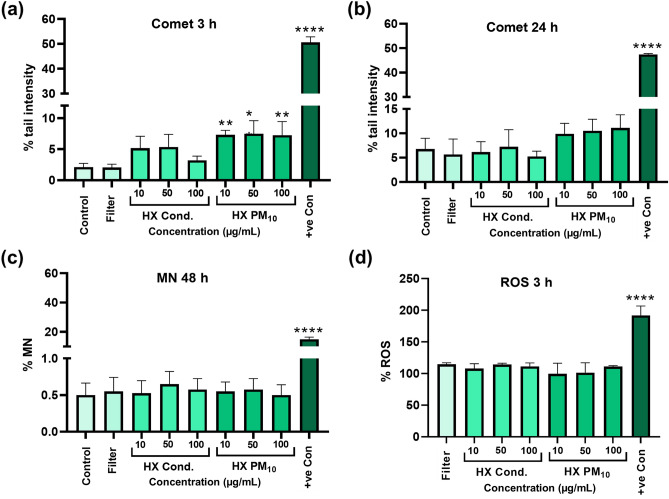
Figure 4.
Genotoxicity assessment and intracellular ROS formation after exposure to the Hastelloy X (HX) condensate particles and the dusted HX collected on filters. The comet assay was used following exposure of HBEC cells for 3 h (a) and 24 h (b). The bars represent the tail intensity (% DNA in the comet tail) and H2O2 (100 μM for 5 min on ice) was used as a positive control. Micronucleus (MN) formation (%) assessment using flow cytometry following 48 h exposure (c). Etoposide (1 µM) was used as positive control. Intracellular ROS formation was determined by using the DCFH-DA assay after 3 h exposure (d). Fe3O4 nanoparticles (50 µg/mL) was used as positive control. The results are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) increase compared to untreated cells (negative control, i.e. medium for the condensate and blank filter extract for the dusted HX collected on filter).