Fig. 2. Sequential epitope mapping identifies CAR45 epitopes on human CD45.
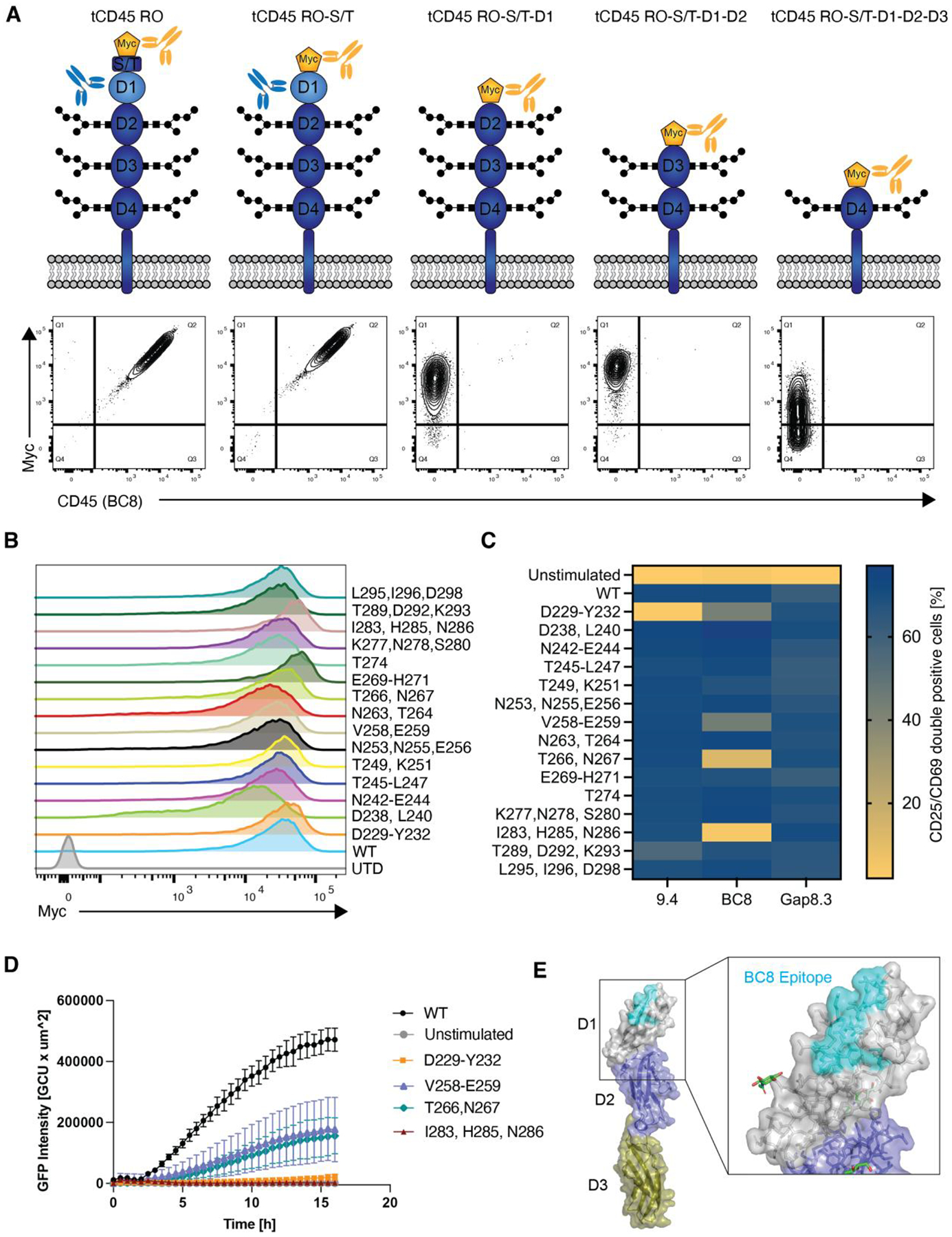
(A) Truncated human CD45 constructs that sequentially lack CD45’s extracellular subdomains were expressed in CD45 negative NALM6 cells. WT CD45RO was expressed as a positive control. Cells were stained with anti-myc to verify surface expression and with clone BC8 to determine CD45 binding. BC8 was mapped to the D1 domain of the CD45 ECD as the BC8 clone no longer bound to the CD45 constructs that lacked this domain. (B) Myc-tagged alanine mutants of the D1 domain were expressed in NALM6 cells. Alanine mutagenesis did not affect protein expression or transport to the cell surface. (C) NALM6 cells expressing either WT or alanine-mutated CD45 were co-cultured with CD45KO CART45 for 24h. Activation of CART45 cells was measured by surface expression of CD25 and CD69. Data are represented as the mean of n=2 technical replicates. (D) Jurkat NFAT-GFP reporter cells expressing the BC8-based CAR were co-cultured with NALM6 cells expressing CD45 alanine mutants and activation was measured by time lapse fluorescence microscopy (n=4 technical replicates). Data are represented as the mean ± SD. (E) Amino acid mutations that decreased BC8 CAR activation compared to CD45WT recognition were superimposed onto CD45 protein structure (PDB ID: 5FMV). BC8 recognizes a conformational epitope on the N-terminal portion of the CD45 D1 domain.
