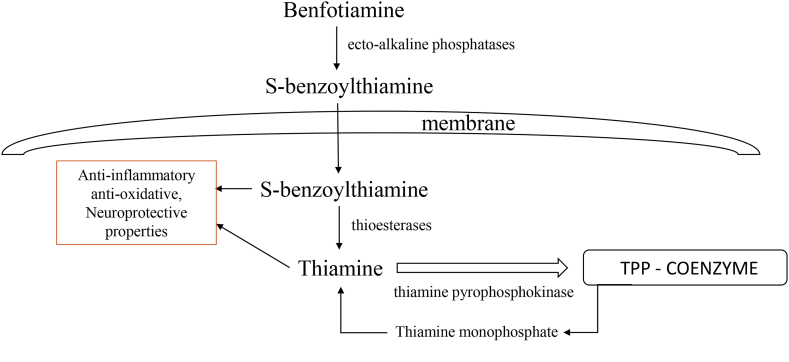
Fig. 3.
The metabolic pathways of benfotiamine. Benfotiamine is dephosphorylated to S-benzoylthiamine by phosphatases present on the cell membrane. S-benzoylthiamine then enters the cell and is converted to thiamine by thioesterases. A portion of thiamine is further phosphorylated by thiamine pyrophosphokinase to TPP that serves as coenzyme in glycolysis, Krebs cycle and pentose phosphate cycle. Thiamine and benfotiamine metabolites show anti-inflammatory, antioxidative and neuroprotective effects.