Figure 1:
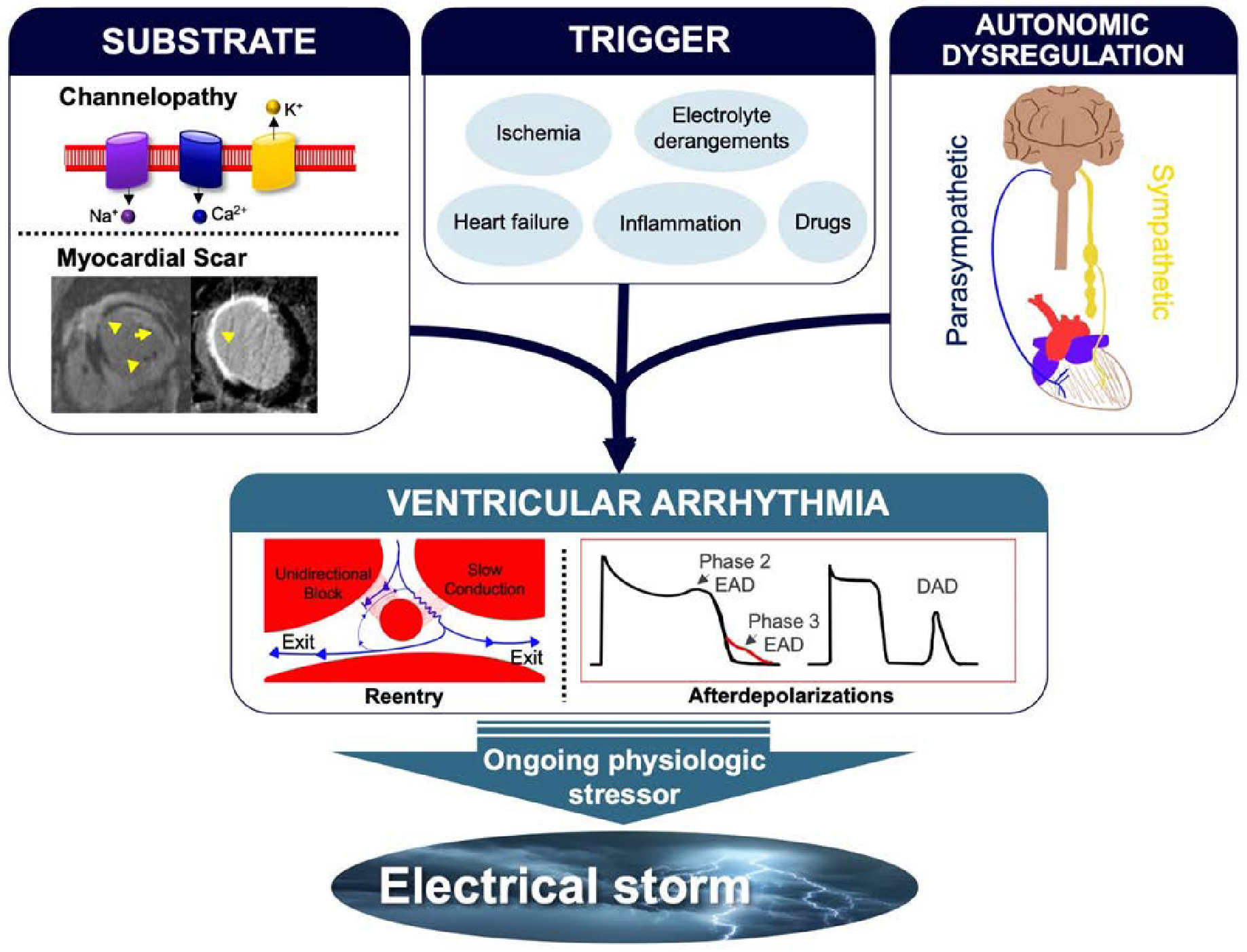
Mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis in ES. Triggers such as myocardial ischemia, inflammation, or hemodynamic decompensation, as well as drug and electrolyte effects, often with accompanying autonomic nervous system imbalance, can lead to sustained VA due to reentry and/or after depolarizations in those with vulnerable anatomic or electrical substrates (e.g., myocardial scar). Perpetuation of the inciting trigger and the resulting sympathetic nervous system response leads to recurrent VA and ES.
