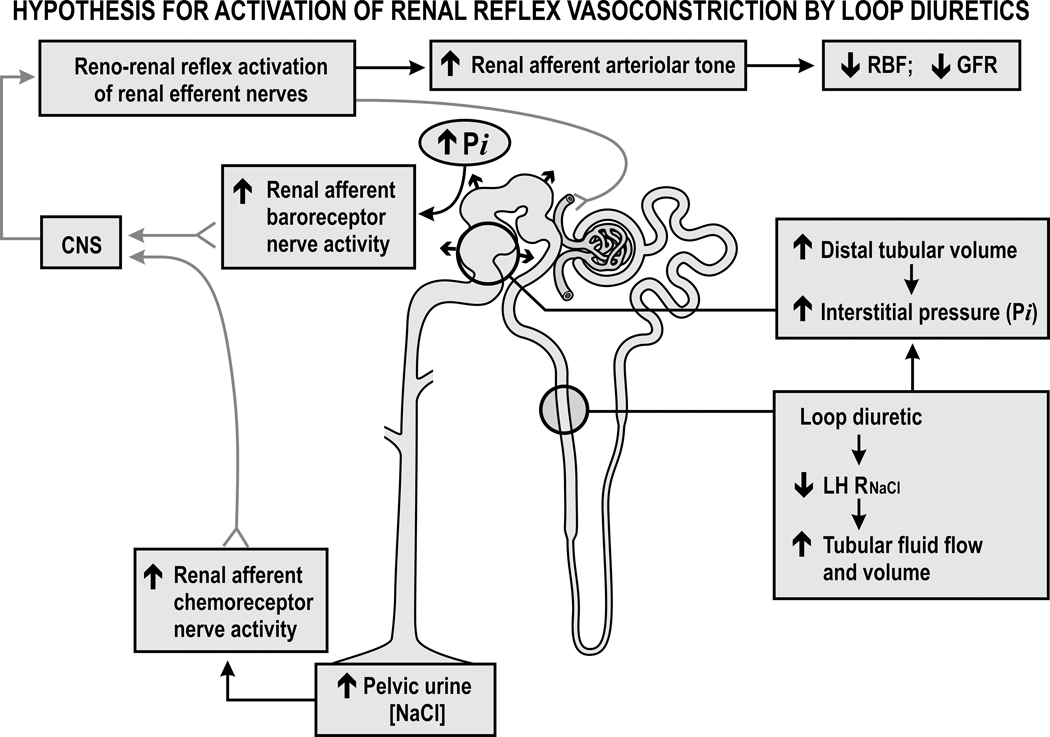
Figure 4. Hypothesis for activation of renal reflex vasoconstriction by loop diuretics:
Diuretics reduce the reabsorption of sodium chloride in the loop of Henle (LH RNaCl), distend the distal tubules and increase the renal interstitial pressure (Pi) that activates renal afferent baroreceptor nerves but also increase the pelvic urine sodium chloride concentration that activates renal afferent chemoreceptor nerves. The increased afferent nerve discharge activates a central nervous system (CNS) reno-renal reflex that increases the renal efferent nerve activity and the afferent arteriolar tone that reduces the renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate.