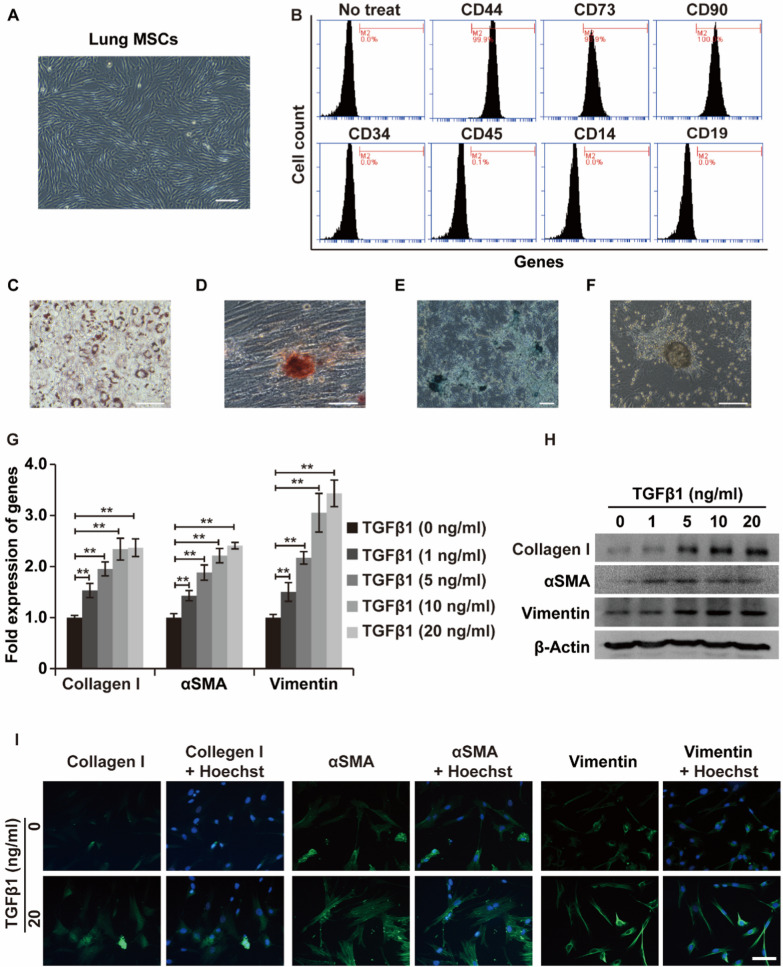
Fig. 1.
LR-MSCs differentiate into myofibroblasts in response to TGF-β1. A Morphologies of mouse LR-MSCs under a standard light microscope. Scale bar: 200 μm. B Flow cytometric analysis of surface markers (CD44, CD73, CD90, CD34, CD45, CD14 and CD19R) on LR-MSCs. C–E Adipogenic (oil red O staining), osteogenic (alizarin red staining) and chondrogenic (alcian blue staining) differentiation potential of LR-MSCs. F Cartilage nodules formed by LR-MSCs during chondrogenic differentiation. G–I Relative changes in the mRNA and protein levels of the indicated markers related to myofibroblast differentiation (α-SMA, type I collagen, and vimentin) in LR-MSCs at baseline and after TGF-β1 stimulation, as assessed by qRT‒PCR, WB assays and immunofluorescence analysis. β-Actin was used as a reference gene. Scale bars = 20 μm, **P < 0.01