Figure 2. Printability characterization of the GelMA/Laponite composite hydrogels.
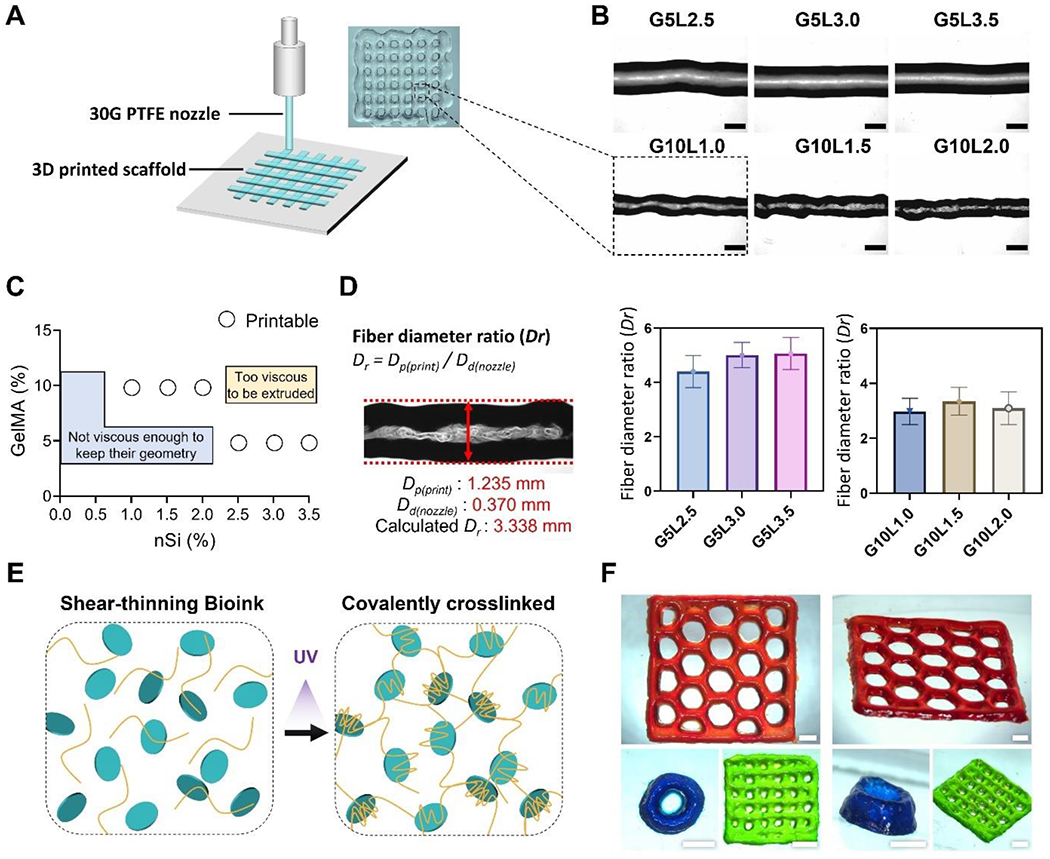
A) Schematic representation of 3D printing process and a digital image of a 3D printed grid structure. B) bright-field microscopy (BF) images of printed fibers from different GelMA/Laponite composite hydrogels (Scale bar: 1 mm). C) Representation of printable and non-printable compositions. D) Fiber diameter ratio (Dr) of GelMA/Laponite composite hydrogels extruded through a 30G PTFE nozzle. Data are means ± SD (n = 10). E) Schematic representation of the shear-thinning GelMA/Laponite composite hydrogel before and after photo-crosslinking. F) Representative digital images of 3D printed multiple layers with different geometries (Scale bar: 2 mm).
