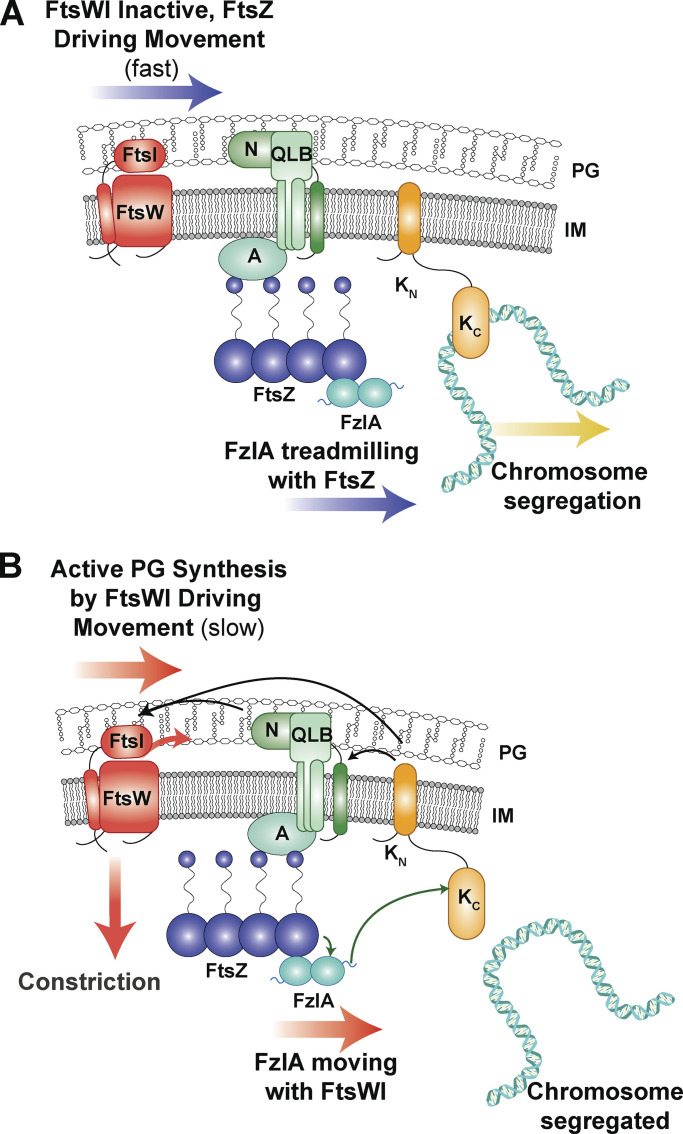
Figure 10.
FzlA binds to FtsZ and signals through FtsK to shift FtsW to a slow-moving, active state. (A) When FtsK is actively segregating chromosomal termini from the division plane, it has limited interaction with FzlA and signaling downstream to activate FtsWI does not occur. Inactive FtsW molecules either move with FtsZ clusters as they treadmill about the division plane or are stationary. FzlA molecules treadmill with FtsZ or remain stationary. (B) When FtsK is not bound to DNA, the FzlA C-terminal tail can bind to FtsKC to signal downstream for FtsWI activation, thereby coupling chromosome segregation to constriction progression. (A and B) Black arrows indicate hypothesized signaling. Green arrows indicate direct interactions confirmed in Caulobacter. Other divisome components depicted for hypothesized downstream interactions: A, FtsA; QLB, FtsQLB complex; N, FtsN.