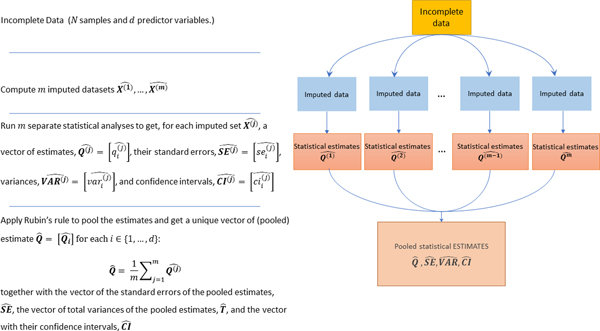
Figure 2:
Schematic diagram of the pipeline used to obtain pooled estimates when applying a MI strategy. The incomplete dataset is imputed times, where the value of can be defined in order to maximize the efficiency of the MI estimator (see Appendix A); each imputed dataset is individually processed to compute separate inferences; all the inferences are pooled by Rubin’s rule [4] to get the pooled estimates (), their total variances () and standard errors () and their confidence intervals (). In the figure, we use the superscript to index the imputations number () and the subscript to index the predictor variable in the dataset (see Table 2 for a detailed list of all the notations used throughout the paper).