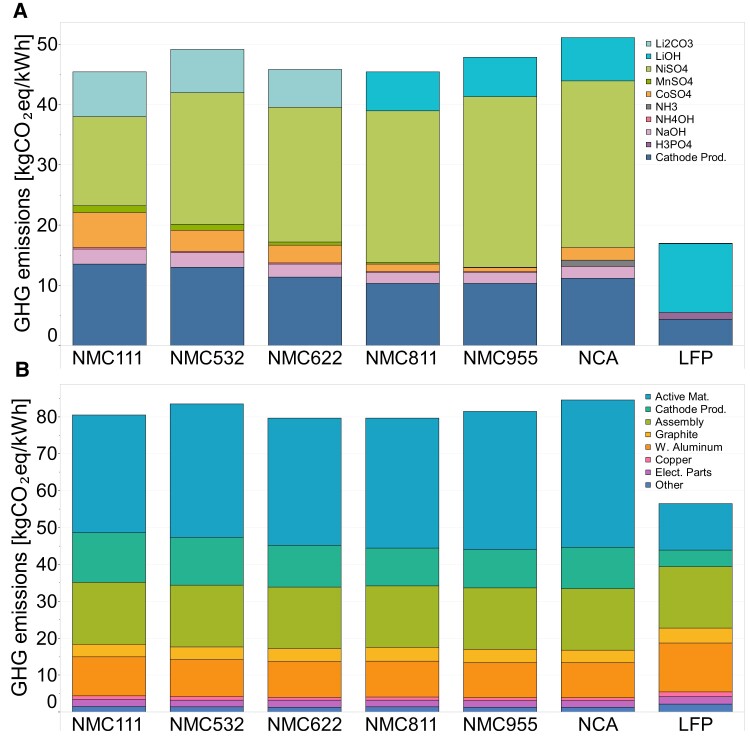
Fig. 1.
Cradle-to-gate GHG emissions of 1 kWh of different LIB technologies and the breakdown of contributions of the materials, along with the bill of material (BOM) (i.e. weights of different materials/components) and battery assembly. (A) Cathode active material. The cathode production process includes precursor co-precipitation and cathode production via calcination. (B) Total battery. Materials such as binder (polyvinylidene fluoride), electrolytes (LiPF6, ethylene carbonate, dimethyl carbonate), plastics (polypropylene, polyethylene, polyethylene terephthalate), steel, thermal insulation, and coolant are grouped into “Other” because they each contribute less than 1% to the total GHG emissions. Numerical data can be found in Tables S10 and S11 in the supplementary information.