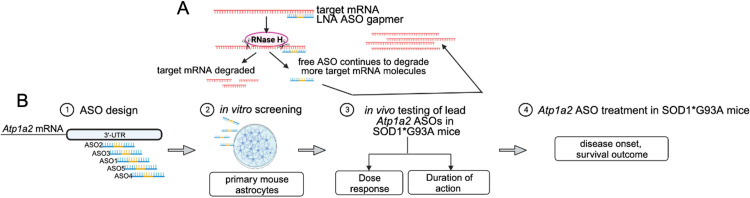
Fig 1. Study overview.
(A) Mechanism of gene knockdown by locked nucleic acid (LNA) antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) employed in this study. (B) Workflow: (1) Five distinct LNA ASO GapmeRs targeting different regions of the 3’-UTR of mouse Atp1a2 were designed, a non-targeting negative control LNA GapmeR (ctrl) was also used in this study to confirm Atp1a2 knockdown-specific effects and rule out general response to LNA oligonucleotides; (2) the five ASOs were screened for their efficiency of Atp1a2 knockdown using primary mouse astrocytes; (3) two ASOs and ctrl were then delivered in a single dose into the central nervous system of SOD1*G93A mice via intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration prior to disease onset to identify the optimal ASO concentration for target knockdown with minimal toxicity; (4) treatment of SOD1*G93A mice prior to disease onset with optimal ASO concentration to evaluate the impact of Atp1a2 knockdown on disease onset and survival.