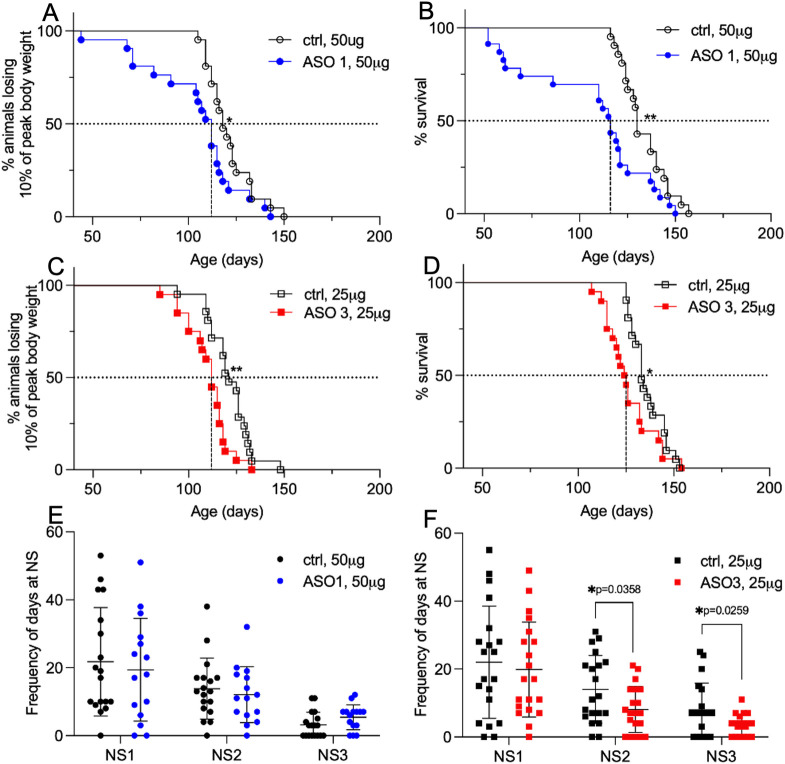
Fig 5. Atp1a2 knockdown in SOD1*G93A mice results in accelerated disease onset and death with ASO3 treatment rescuing hindlimb motor function.
Disease onset was defined as the age at which animals lose 10% of their peak body weight. (A) Median disease onset for ASO1-treated mice was 112 days compared with ctrl ASO-treated mice (118 days). (B) Median disease onset for ASO3-treated mice was 112 days compared with ctrl ASO-treated mice (121 days). Disease end-stage was defined as that point at which mice could not right themselves when placed on their side within 30s. (C) The median survival of SOD1*G93A mice treated with ASO1 was 116 days compared with ctrl ASO-treated mice (130 days). (D) The median survival of SOD1*G93A mice treated with ASO3 was 124.5 days compared with ctrl ASO-treated mice (133 days). Log-rank Mantel-Cox test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (E, F) Neurological scoring (NS) system adopted from ALS TDI to assess hindlimb function in SOD1*G93A mice- NS1: first symptoms (abnormal splay and/or tremble during tail suspension test), NS2: onset of paresis and NS3: paralysis. Frequency of days spent at NS stage for Atp1a2 ASO1 and the ctrl ASO-treated mice (E, n = 15 mice) or Atp1a2 ASO3 and the ctrl ASO-treated mice (F, n = 18 mice). n used for A-D as indicated in Fig 4A legend. Unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction, *p<0.05.