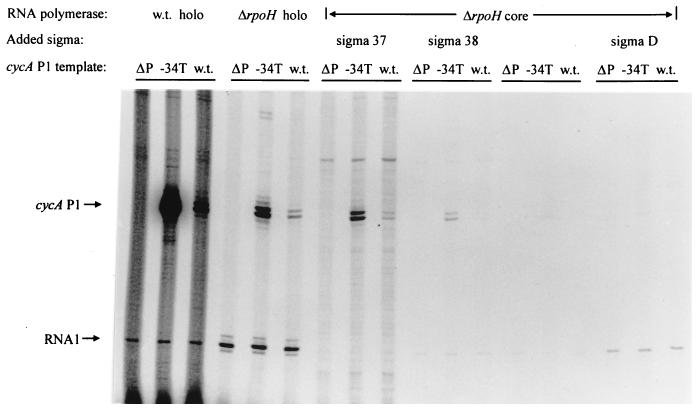
FIG. 3.
Transcription of wild-type cycA P1 and G34T templates by individual RNA polymerase holoenzymes. Templates which lack the cycA P1 sequence (ΔP), the wild-type cycA P1 promoter (w.t.), or the G34T (−34T) mutation in the cycA P1 promoter were used as indicated directly above the gel. Above each set of lanes (ΔP, −34T, and w.t.) is indicated the source of RNA polymerase holoenzyme (w.t. holo, holoenzyme preparations from wild-type cells; ΔrpoH holo, analogous material from a ΔRpoH mutant [11]; ΔrpoH core, core RNA polymerase from a ΔRpoH mutant). For assays where core RNA polymerase was reconstituted with potential sigma subunits, ς37 and ςD were obtained from a wild-type RNA polymerase sample (fractions 9 and 19, respectively, in Fig. 4A). ς38 was obtained from the ΔRpoH RNA polymerase sample (fraction 20 in Fig. 4B). The positions of transcripts (arrows) are indicated as follows: RNA1, the EςD-dependent transcript from the oriV promoter present on all templates (10); cycA P1, the specific cycA transcript produced by templates that contain wild-type or G34T mutant promoters.