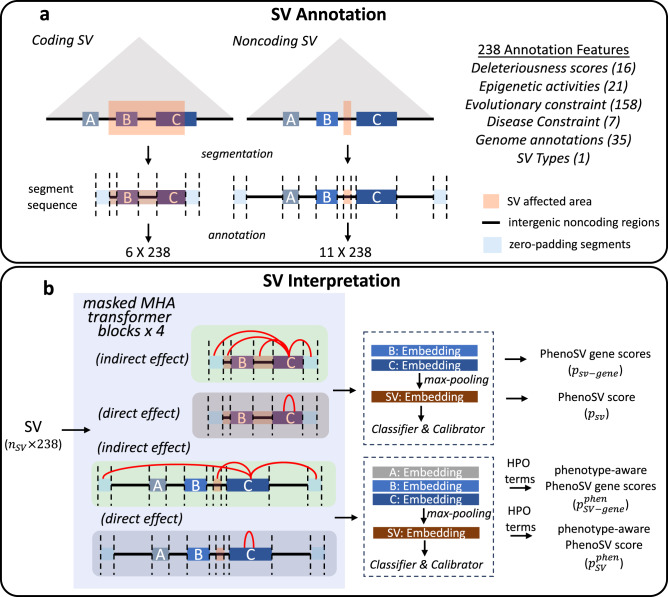
Fig. 1. PhenoSV workflow.
a SV annotation. A coding SV that is a deletion or a duplication, fully containing gene B and partially encompassing gene C, is segmented into a sequence of six genome segments, including two affected genes, two intergenic noncoding regions, and two zero-padding segments. A noncoding SV that is a deletion or a duplication can potentially affect gene A, B, and C based on distance or TAD annotations (triangle shaded area). The genomic segment sequence has three candidate target genes, five intergenic noncoding regions, a noncoding SV region, and two zero-padding segments. b SV interpretation. Annotated SV with the shape of 6 ×238 or 11 ×238 from (a) is fed into PhenoSV architecture. Each MHA (multi-head attention) block has two types of attention heads to model indirect and direct effects on genes. The pathogenicity for overall SV (PhenoSV scores, ) and individual genes (PhenoSV gene scores, ) can be inferred from SV-level and gene-level embeddings, respectively. Prior phenotype information (HPO terms) can be further used to infer phenotype-related pathogenicity for overall SV (phenotype-aware PhenoSV scores, ) and individual genes (phenotype-aware PhenoSV gene scores, ).