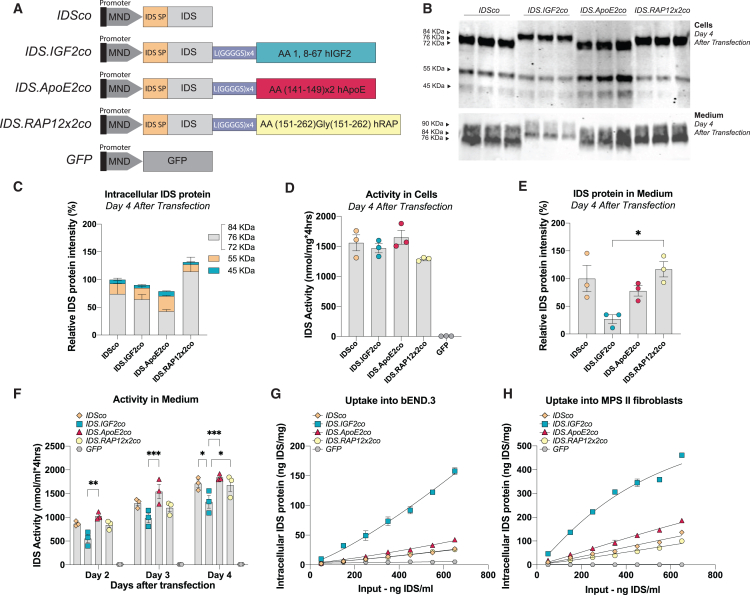
Figure 1.
In vitro characterization of tagged IDS proteins
(A) Cartoons of pCCL third-generation lentiviral vectors encoding codon optimized (co) human IDS proteins under the control of the MND promoter. Human IDS was either not tagged or tagged C-terminally with IGF2 (IDS.IGF2co), ApoE2 (IDS.ApoE2), or RAP12x2 (IDS.RAP12x2co). An identical lentiviral vector encoding GFP served as control. IDS SP, IDS signal peptide; hIGF2, human insulin-like growth factor 2; hApoE, human apolipoprotein E; hRAP, human receptor-associated protein. (B–F) HEK293T cells were transfected with lentiviral vectors shown in (A). (B) Immunoblot analysis using an anti-IDS antibody of cell lysate and medium at day 4 after transfection. Three biological replicas are shown. Quantification of (B) is shown in (C and E). Protein loading was determined by quantification of the stain-free signal (Figure S1A) and was used for normalization. (D) Intracellular IDS enzyme activity at day 4 after transfection. (F) IDS enzyme activity in medium at days 2, 3, and 4 after transfection. Data in (C)–(F) were normalized for transfection efficiency (Figure S1D). Captured IDS protein using IDS sandwich ELISA after 24 h uptake into bEND.3 cells (G) and MPS II fibroblasts (H). Data in (C), (E), (G), and (H) were quantified within the IDS antibody linear range (Figure S1C). Data represent means ± SEM and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple testing correction. n = 3 biological replicates/condition. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001. Significant comparisons are indicated by brackets.