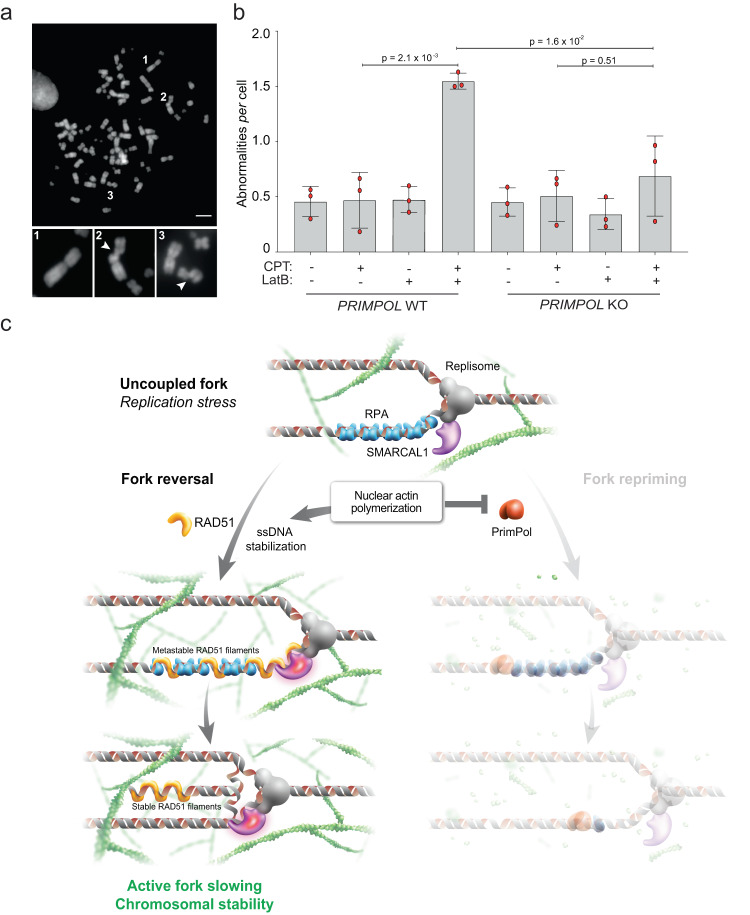
Fig. 6. Nuclear F-actin limits chromosomal instability upon genotoxic treatments by limiting PrimPol function and promoting efficient fork remodeling.
a Representative metaphase spread image. Scale-bar = 5 μm. 1 = representative intact chromosome. 2, 3 = representative breaks. b Number of chromosomal abnormalities in U2OS cells (proficient for (WT) or lacking (KO) PRIMPOL) optionally treated with 100 nM CPT for 2 h. Where indicated, 100 nM LatB was added 10 min before CPT and retained. Bar graph depicts mean ± SD from three independent experiments (red dots). A minimum of 30 metaphases was analyzed per sample and experiment. Statistical analysis: one-way ordinary ANOVA. c Working model: nuclear F-actin polymerization limits PrimPol recruitment to uncoupled replication forks, stabilizing ssDNA stretches. This facilitates RAD51 recruitment to stalled/uncoupled forks and promotes SMARCAL1-dependent fork reversal, mediating active fork slowing and protecting the integrity of replicating chromosomes. A graphical representation of the consequences of defective nuclear actin polymerization is depicted in Supplementary Fig. 6c (see Discussion for details). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.