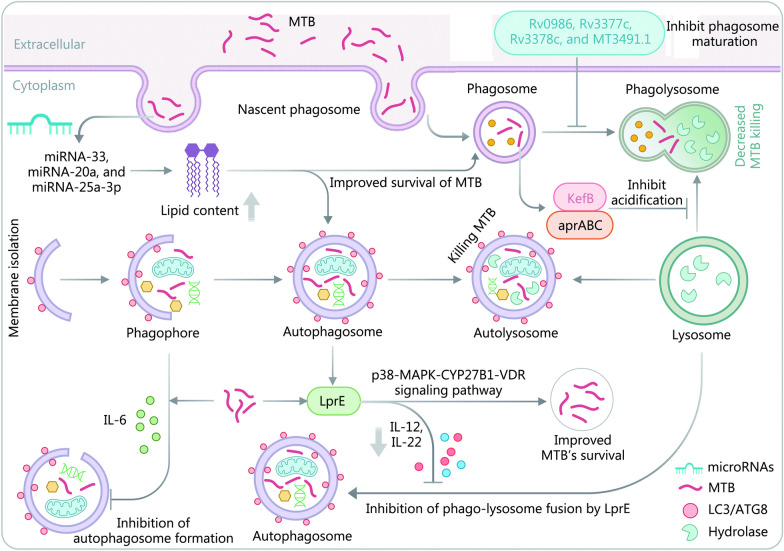
Fig. 5.
Evasion of autophagic-lysosomal and phagocytic-lysosomal killing by MTB. The bactericidal process of autophagic-lysosomal degradation involves the formation of autophagic precursors that engulf the infected cells to create autophagosomes which then fuse with lysosomes. This results in the hydrolysis of infected cells by lysosomal enzymes. However, in the presence of toxic MTB, the formation of autophagic precursors is inhibited through the regulation of cytokine production. Additionally, MTB’s lipoproteins LprE can delay the fusion of phagocytic lysosomes by regulating cytokines production, leading to the evasion of phagocytic-lysosomal killing. The phagocytic process involves the engulfment of MTB vesicles by lysosomes containing acid hydrolases that can kill MTB. MTB evades phagocytic-lysosomal killing in various ways. MTB Mycobacterium tuberculosis, IL interleukin, KefB a potassium/proton antiporter in MTB (Rv3236c), aprABC an MTB complex-specific locus, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, CYP27B1 1 alpha-hydroxylase, VDR vitamin D receptor, LC microtubule-associated protein light chain, ATG8 autophagy associated proteins 8