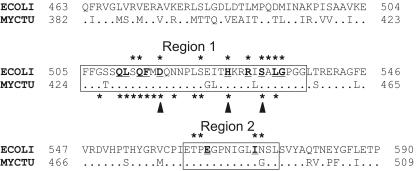
FIG. 1.
Alignment of the β-subunit RIF regions of E. coli (ECOLI) and M. tuberculosis (MYCTU) RNAPs. Dots in the sequence of M. tuberculosis represent amino acids that are identical to those of E. coli. Numbers on both sides of the sequences indicate the positions of amino acids starting from the N terminus of the protein. The first and the second RIF regions are boxed. Positions of the Rifr mutations are marked with asterisks; mutations in E. coli and M. tuberculosis RNAPs are shown above and below the alignment, respectively. Amino acids that directly interact with RIF in the structure of T. aquaticus RNAP (2) are bold and underlined. Three positions of the first RIF region which most frequently mutate in M. tuberculosis are indicated by arrowheads under the sequence.