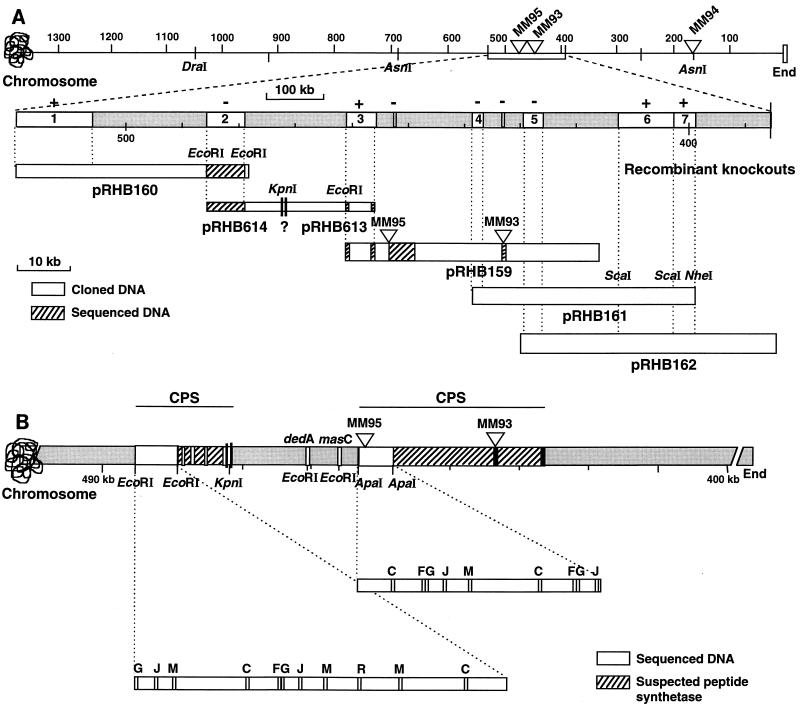
FIG. 2.
Partial physical map of the daptomycin gene cluster. (A) The top line shows the locations of the Tn5099 insertions (triangles) within the 1,050-kb DraI-C fragment and the 490-kb AsnI-E fragment relative to the end of the chromosome in strains MM95, MM93, and MM94. The region containing the insertions in MM95 and MM93 is expanded below to show the overlapping cosmid inserts (pRHB159, pRHB160, pRHB161, and pRHB162) and plasmids (pRHB614 and pRHB613) that span the peptide synthetase coding region. The segments in white marked 1 through 7 represent subcloned fragments used for gene disruption analysis. Recombinants were analyzed for daptomycin production (+ or − above the segments). The cross-hatched segments were sequenced. (B) Summary of the partial DNA sequencing of the daptomycin cluster. The 7.9-kb EcoRI fragment contains motifs present on peptide synthetase modules that activate and epimerize amino acids (33). The 5.3-kb ApaI fragment contains motifs found in modules that activate l-amino acids (33). The lines above the map summarize the locations of two regions encoding cyclic peptide synthetase (CPS) subunits that are separated by a region containing dedA and masC homologs.