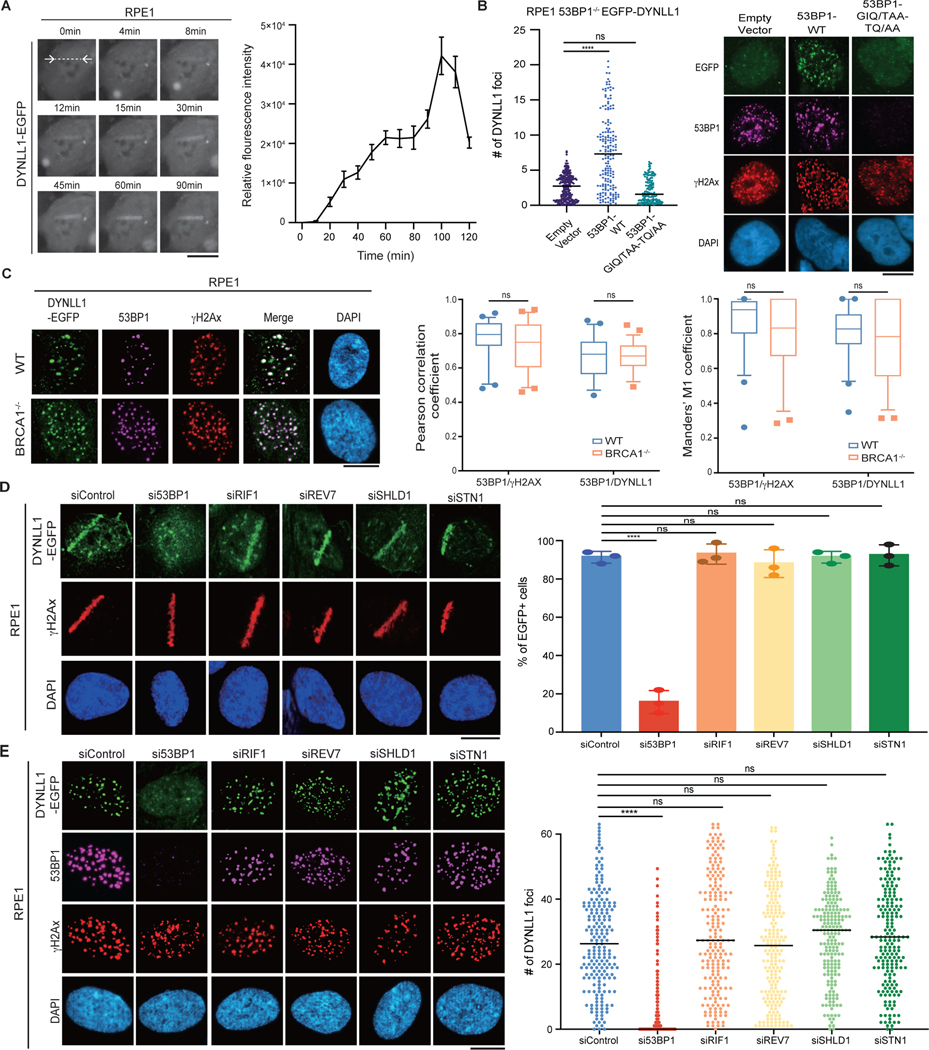
Fig. 1 |. DYNLL1 recruitment to DSBs is dependent on 53BP1 but independent of other 53BP1-associated factors.
a, Representative live cell images of RPE1 cells expressing DYNLL1-EGFP after laser microirradiation. b, RPE1 53BP1−/− cells coexpressing EGFP-DYNLL1 and 53BP1–DYNLL1-binding mutants were subjected to 2 Gy of irradiation and 2 h later were processed for immunofluorescence. c, Representative immunofluorescent images of wild-type (WT) RPE1 or BRCA1−/− cells 2 h after exposure to 2 Gy of irradiation. Box plots show the mean, upper and lower quartiles (boxes) and range (whiskers). d,e, Representative images of RPE1 cells coexpressing EGFP-tagged DYNLL1 and short interfering RNA (siRNA) constructs and subjected to laser microirradiation (d) or 2 Gy of irradiation (e) and fixed 1 h later. siControl denotes siRNA against non-targeting control. In a–e, n = 3 biologically independent experiments, counting at least 100 cells per experiment. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. P values were determined by Mann–Whitney test (b, c, e) or two-sided unpaired t-tests (d). ****P < 0.0001.
NS, not significant (P < 0.05). Black lines in dot plots represent the median. DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Scale bars, 20 μm.