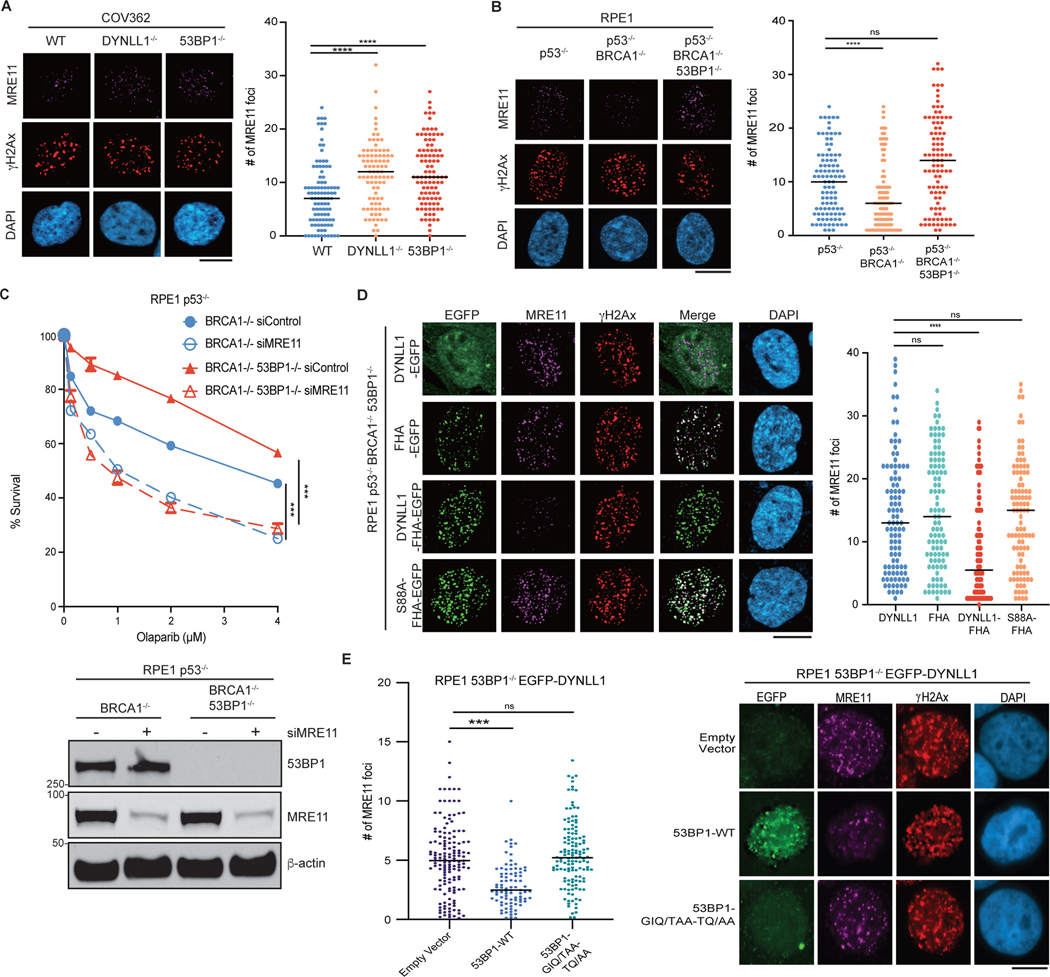
Fig. 2: DYNLL1 regulates MRE11 activity independent of 53BP1.
a,b, COV362 cells depleted of DYNLL1 or 53BP1 (a) and RPE1 cells depleted of p53, BRCA1 and/or 53BP1 (b) using CRISPR–Cas9 were exposed to 2 Gy of irradiation for 2 h. Cells were fixed and immunostained using antibodies against MRE11 and γH2AX. c, RPE1 p53−/− BRCA1−/− and p53−/− BRCA1−/− 53BP1−/− cells were depleted of MRE11 using siRNA (siMRE11), and treated with indicated concentrations of olaparib for 6 days. Survival was determined via a cell viability assay (top), and a representative western blot shows successful knockdown of MRE11 using siRNA (bottom). d, Immunofluorescence of RPE1 p53−/− BRCA1−/− 53BP1−/− cells expressing EGFP-tagged DYNLL1 constructs exposed to 2 Gy of irradiation for 2 h, and stained using antibodies against MRE11, GFP (DYNLL1) and γH2AX.
e, Immunofluorescence of RPE1 53BP1−/− cells coexpressing EGFP-DYNLL1 and 53BP1–DYNLL1-binding mutants exposed to 2 Gy of irradiation for 2 h, and stained using antibodies against MRE11, 53BP1 and γH2AX. In a–e, n = 3 biologically independent experiments, counting at least 100 cells per experiment. P values determined by two-sided unpaired t-tests (a,b,d,e) or nonregression curve analysis (c). ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Black lines in dot plots represent medians. Scale bars, 20 μm.