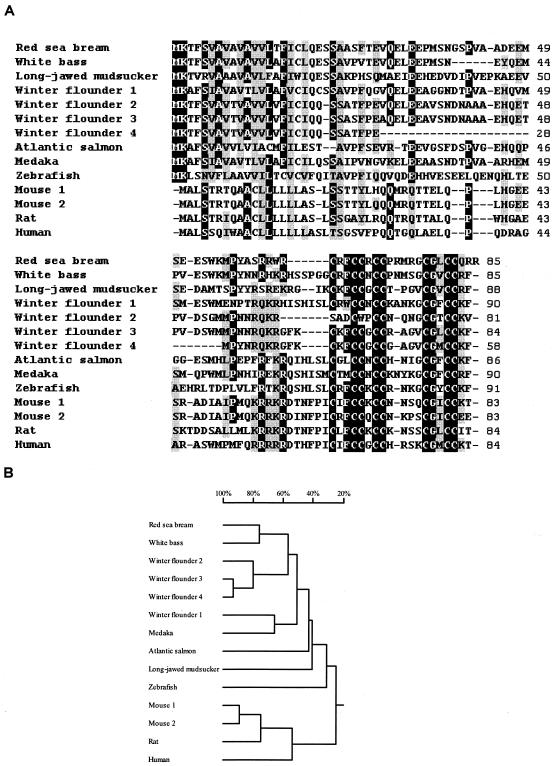
FIG. 2.
Alignment of the red sea bream hepcidin amino acid sequence with other vertebrate sequences (A) and phylogenetic analysis (B). Numbers to the right of the alignment refer to positions found in the sequences. Identical or similar amino acid residues are black or shaded. Dashes, gaps used to maximize the alignment. Sources of sequences used for comparison, with references for GenBank accession numbers or the number itself in parentheses, are as follows: white bass (24), winter flounder 3 (12), winter flounder 2 (12), medaka (AU178966), winter flounder 1 (12), long-jawed mudsuckers (13), winter flounder 4 (12), Atlantic salmon (12), zebra fish (25), mouse 1 (14), mouse 2 (14), rats (22), and humans (22). Cluster analysis (B) is based on the deduced amino acid sequence of hepcidin from red sea bream and other vertebrates. The scale over the tree refers to the percentage of divergence.