Fig. 6 |. An integrated multiomics approach.
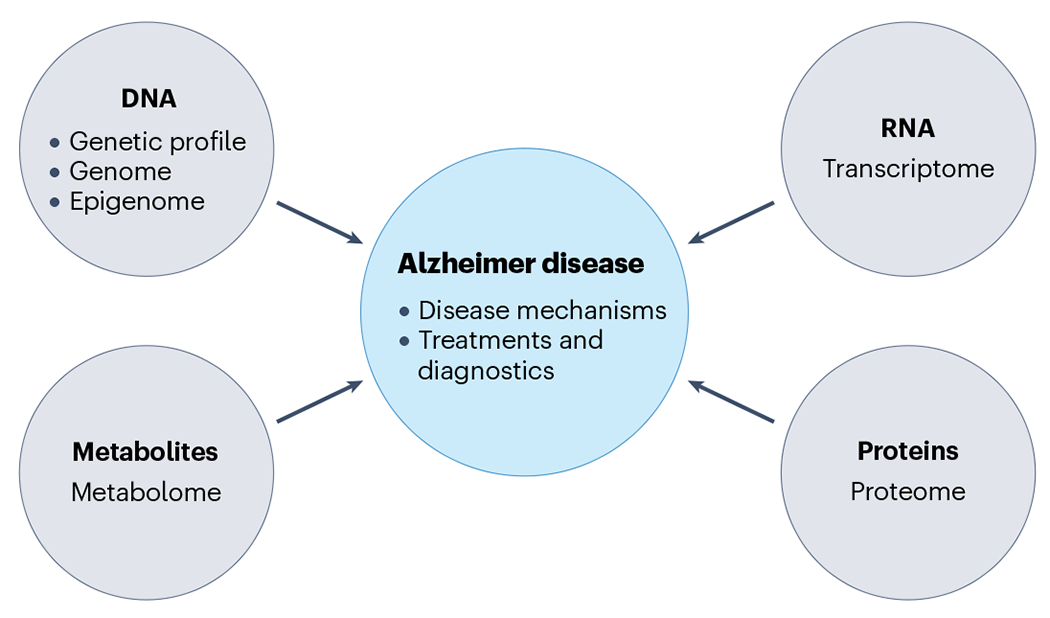
Integrated multiomics approaches can be used to understand how genetic variation leads to disease, to establish which molecular pathways are altered, and to identify new therapeutic targets and diagnostic approaches. Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) would be generated from each omics layer (gene expression from the transcriptome, protein quantitative traits from the proteome, methylation quantitative traits from the metabolome). These multiomics layers would then be integrated into a systems analysis that includes information on the genome and epigenome, with the goal of furthering understanding of disease mechanisms and developing novel treatments and diagnostics.
