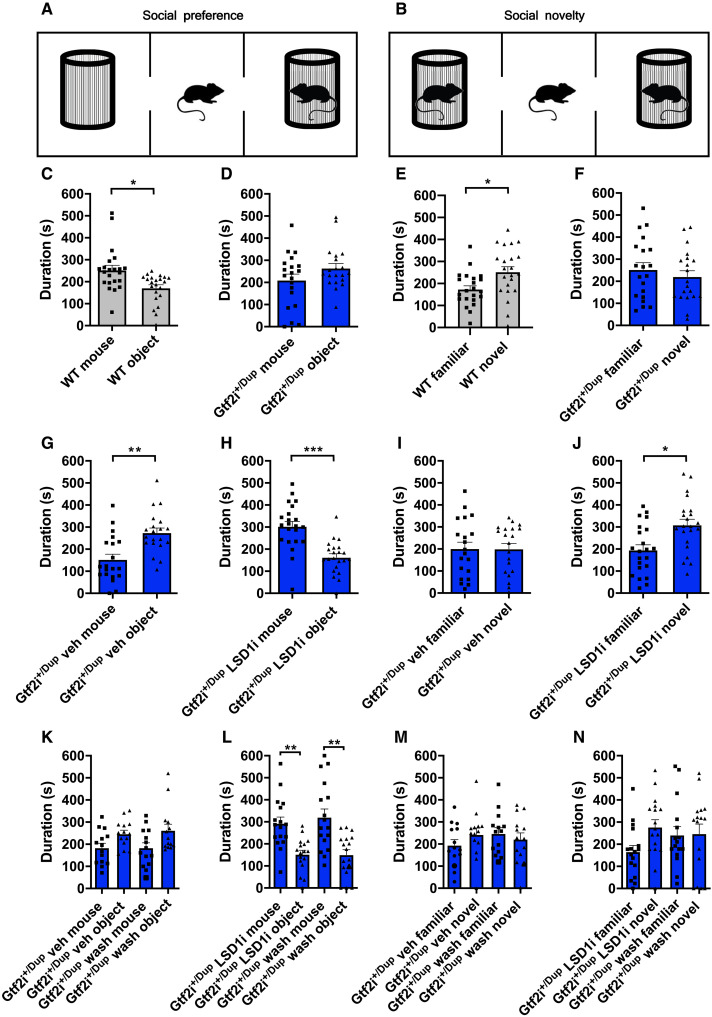
Fig. 6. Inhibition of LSD1 rescues ASD-like phenotypes in Gtf2i+/Dup.
(A and B) Schematic representation of the three-chamber sociability apparatus for measuring social preference and social novelty, respectively, in male mice. (C to F) Bar plots with dots depicting the time spent with a conspecific versus object and with a novel versus familiar mouse at baseline, in WT (n = 22) and Gtf2i+/Dup (n = 20) mice. (G to J) Bar plots with dots depicting the time spent with a conspecific versus object and with a novel versus familiar mouse in Gtf2i+/Dup mice following four oral gavage administrations (two times per week over 2 weeks) of vehicle (n = 20) or LSD1 inhibitor (10 mg/kg; n = 22). (K to N) Bar plots with dots depicting social preference and social novelty results in Gtf2i+/Dup mice tested after the fourth administration of vehicle (n = 14) or LSD1 inhibitor (n = 17) and after a 2-week washout period. Data are shown as means ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using paired Student’s t test, followed by Holm-Bonferroni correction for multiple testing, except for (C), (I), and (M), where the data did not have a normal distribution and Wilcoxon signed rank test was used instead. Significance level P < 0.05. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.