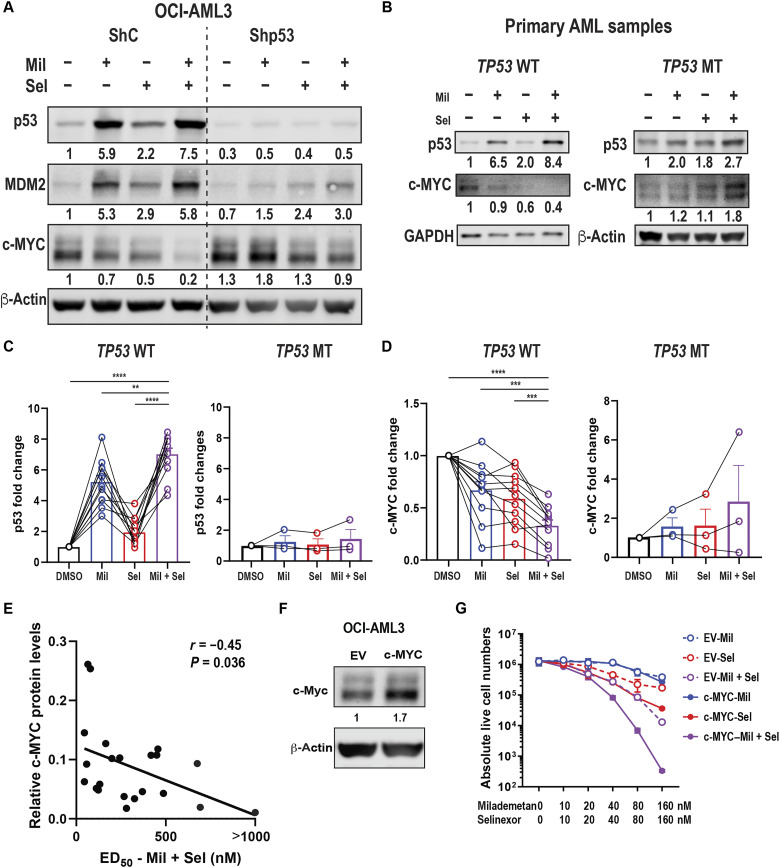
Fig. 3. Dual MDM2/XPO1 inhibition–mediated c-MYC reduction is p53 dependent and baseline c-MYC protein levels correlate with sensitivity to Mil + Sel.
(A) Immunoblot of p53, MDM2, and c-MYC in OCI-AML3 cells transfected with shRNA for scramble control (ShC) and p53 knockdown (Shp53) treated with Mil, Sel, or Mil + Sel for 12 hours. (B) Immunoblot of p53, MDM2, and c-MYC of TP53 wild-type (WT) and mutant (MT) primary AML samples treated with Mil, Sel, or Mil + Sel. (C) Protein levels of p53 in 10 TP53 WT (left) and 3 TP53 MT (right) primary AML samples. (D) Protein levels of c-MYC in 10 and 3 WT (left) and MT (right) TP53 primary AML samples. Data in (C) and (D) represent means ± SEM values. (E) The correlational plot of baseline c-MYC protein levels and ED50 values for Mil + Sel in primary AML samples. (F) Immunoblot of c-MYC in OCI-AML3 cells transfected with empty vector (EV) control or MYC-overexpressing plasmids (c-MYC). (G) Live cell numbers in OCI-AML3 EV and c-MYC cells treated with Mil, Sel, or Mil + Sel for 72 hours. A Mil and Sel concentration of 160 nM was used. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.