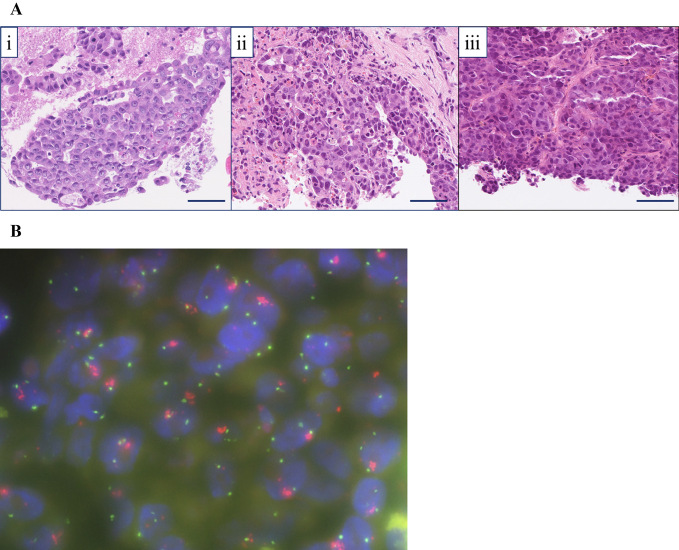
Figure 3.
(A) Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining sample of the metastatic tumor. Each tissue sample had similar tumor cell characteristics. i) Lymph node metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma (EBUS-TBNA, H&E staining, ×200): the specimen showed the proliferation of atypical epithelial cells arranged in a tubular or cribriform growth fashion. ii) Liver metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma (needle biopsy in March 20XX, H&E staining, ×200): atypical epithelial cells arranged in a tubular or cribriform growth fashion were seen (immunohistochemically, the atypical cells were diffusely positive for TTF-1, Napsin A, and ALK and negative for synaptophysin and INSM-1). iii) Liver metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma (needle biopsy in Aug 20XX, H&E staining, ×200): the specimen revealed a proliferation of atypical epithelial cells arranged in nests, sheets, or a trabecular growth fashion (immunohistochemically, the atypical cells were diffusely positive for TTF-1, Napsin A, and ALK and negative for synaptophysin and INSM-1). Scale bar=50 μm. (B) A MET/CEP7 FISH assay (red signal: MET gene; green signal: CEP7). This representative case with MET/CEP7 5.6 (≥5) was classified as having high-level MET amplification. EBUS-TBNA: endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration, TTF-1: thyroid transcription factor-1, INSM-1: insulinoma-associated protein 1, MET/CEP7: ratio of MET to centromere chromosome 7 probe, CEP7: centromere of chromosome 7, FISH: fluorescence in-situ hybridization