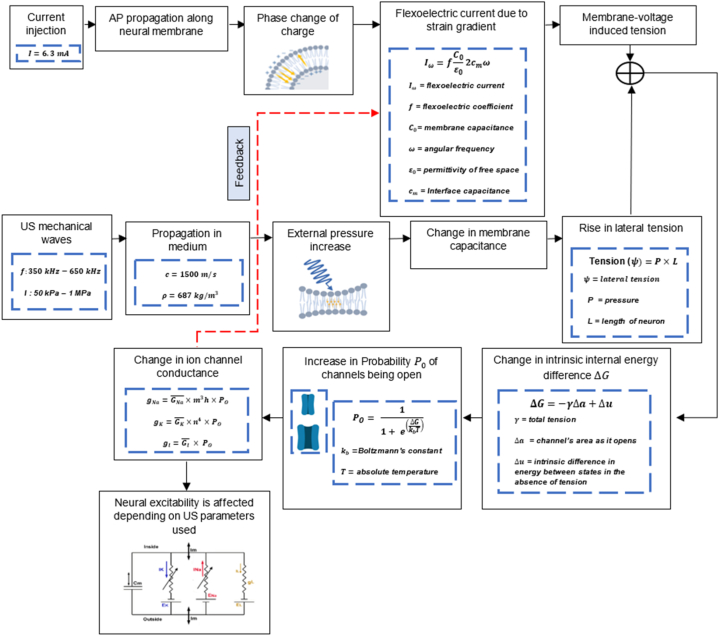
Fig. 3.
Flow chart illustrating the model components. The injected current and the flexoelectric current generated from the viscoelastic nature of the lipid bilayer create a membrane-voltage induced tension. Adding the latter to the lateral tension induced by the external pressure generated from the ultrasound mechanical waves causes a change in the intrinsic energy difference. This increases the probability of ion channels being open thus changing their conductance. As a result, neural excitability is affected and manifested with different firing rates, latencies, and action potential amplitudes. Note that all the components are in a continuous feedback loop whereby a change in the conductance due to ultrasound waves affects the membrane potential which in turn produces a flexoelectric current.