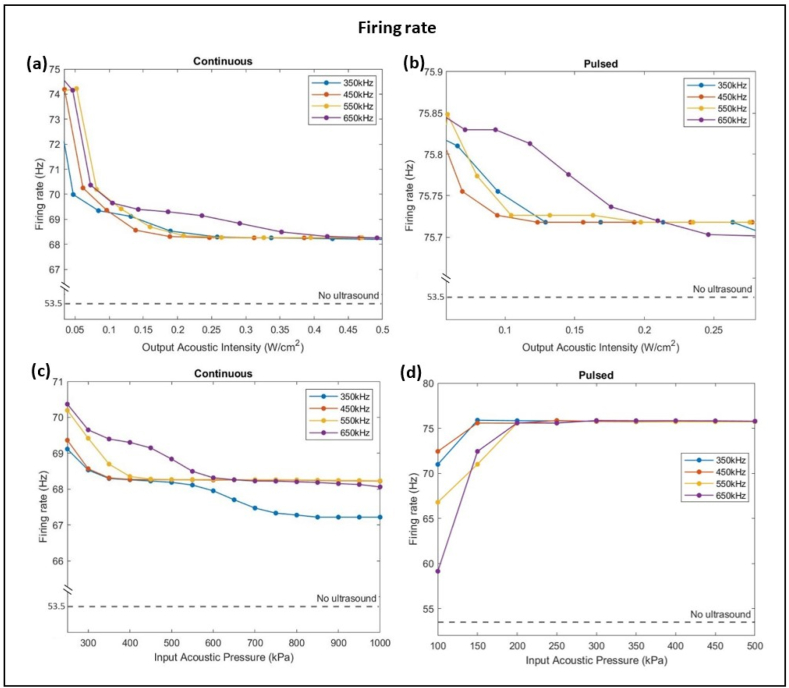
Fig. 4.
Variation of firing rate with respect to frequency, acoustic intensity (a & b), and acoustic pressure (c & d) of ultrasound stimulation in both continuous and pulsed modes. Increasing the acoustic intensity causes a decrease in firing rate to lower values of 67 Hz with continuous ultrasound waves (a) than with pulsed waves of 75.7 Hz (b). However, as the input pressure increases, the firing rate decreases to a minimum of about 67 Hz with continuous ultrasound waves (c), yet it increases to a maximum of 76 Hz with pulsed ultrasound waves (d). The dashed line represents the reference firing rate of a firing neuron when no ultrasound sonication was applied.