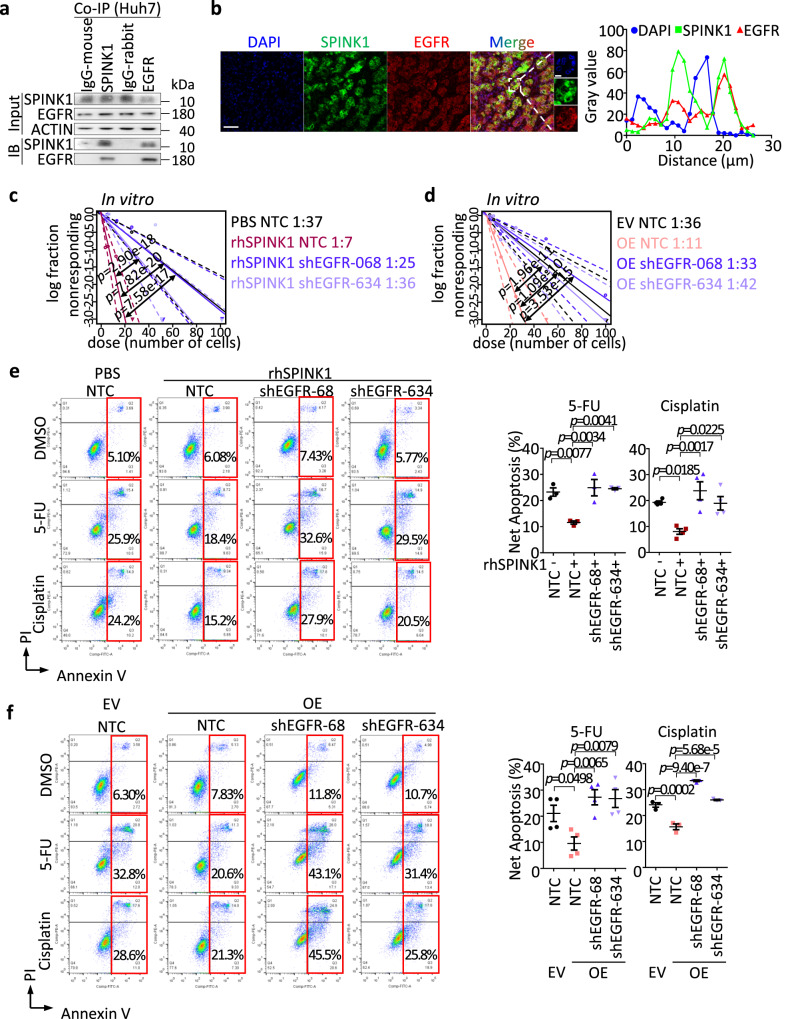
Fig. 6. EGFR is critical for SPINK1 to drive HCC.
a Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analysis for validation of EGFR as an interacting protein partner of SPINK1 in Huh7 cells. IgG-mouse = Mouse isotype control antibody; IgG-rabbit = Rabbit isotype control antibody; IB = Immunoblotting. b (Left) Co-staining of SPINK1 (green) and EGFR (red) protein in human HCC tumor by multiplex immunohistochemistry (IHC). DAPI (blue), nucleus. Scale bar: 50μm. (Right) Histogram representation of line scan analysis for quantification of SPINK1 (green, ■), EGFR (red, ▲) and DAPI (blue, ●). c, d In vitro limiting dilution analysis for frequency of TICs of c MHCC97L with rhSPINK1 treatment or d SPINK1 overexpression (OE) in the presence or absence of shRNA against EGFR stably transduced (shEGFR-068 and shEGFR-634). e, f Cell apoptosis upon 5-FU or cisplatin treatment as demonstrated by Annexin V-PI flow cytometry analysis, in e MHCC97L cells treated with rhSPINK1 or f with SPINK1 overexpression in the presence or absence of EGFR knockdown. a n = 3 independent experiment; b n = 2 human HCC tumor samples; c, d 30 replicates in 3 independent experiments; e n = 3 independent experiments for 5-FU group, 4 independent experiments for cisplatin group; f n = 4 independent experiments for 5-FU group, 3 independent experiments for cisplatin groups. Data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical analysis: c, d one-sided Person’s χ2 test with 95% confidence intervals, or e, f one-way ANOVA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.