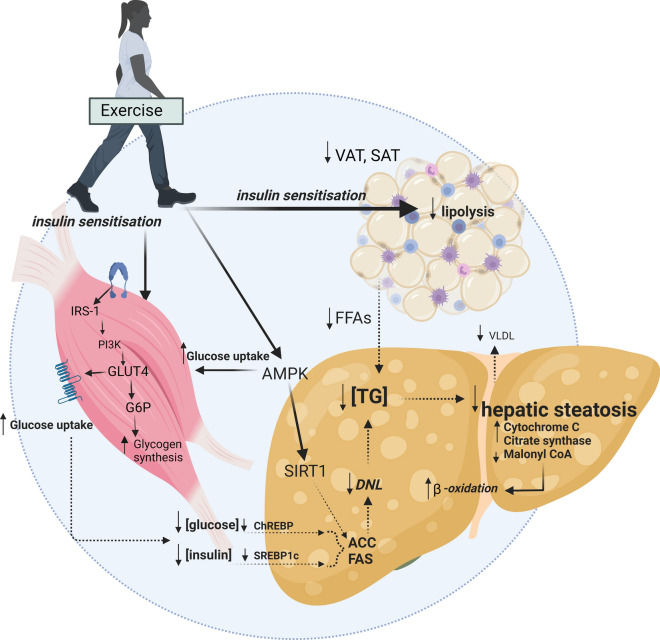
Fig. 3.
Putative mechanisms for the effects of exercise on reducing hepatic steatosis Solid lines indicate enhanced mechanisms (e.g. insulin sensitisation). Dashed lines indicate reduced mechanisms (e.g. reduced concentrations of plasma insulin and glucose, reduced de novo lipogenesis). VAT visceral adipose tissue, SAT subcutaneous adipose tissue, FFA free fatty acid, TG triglyceride, SREBP- 1c sterol regulatory element binding protein, ChREBP carbohydrate responsive element binding protein, DNL de novo lipogenesis, FAS fatty acid synthase, ACC acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase, VLDL very low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, AMPK adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, SIRT1 sirtuin 1, IRS-1 insulin receptor substrate 1, PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, GLUT4 glucose transporter type 4, G6P glucose 6-phosphate. Created with BioRender.com