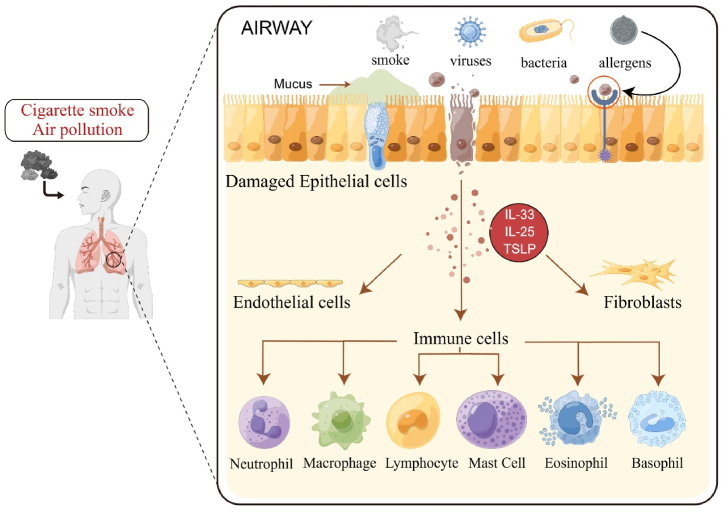
Fig. 1.
Diagrammatic representation of COPD etiology and pathogenesis. Risk factors for COPD include smoking and air pollution, and so on. When irritants and toxicants are inhaled, the structural cells of the lung, such as epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells, get activated. When bronchial epithelial cells are damaged, alarm molecules (TSLP, IL-33, IL-25) are released, activating a variety of immune cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. These cells release inflammatory mediators, which attract other inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes to the exposed area, resulting in persistent airway inflammation.