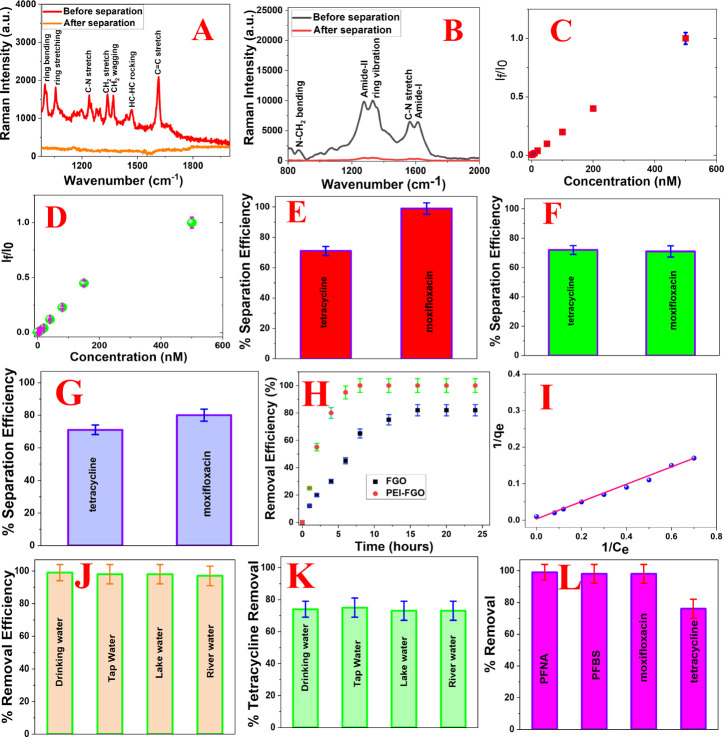
Figure 4.
(A) Surface enhanced Raman spectra (SERS) from water samples of moxifloxacin antibiotics (1000 ng/L) before filtration. SERS from water samples after filtration using the FGO-PEI based nanoplatform. (B) SERS from water samples of tetracycline antibiotics (1000 ng/L) before filtration. SERS from water samples after filtration using the FGO-PEI based nanoplatform. (C) Plot shows how the SERS intensity at 1620 cm–1 for the C=C stretch from moxifloxacin antibiotics varies with the concentration (ng/L). I0 is the SERS intensity at 1620 cm–1 when the concentration is 1000 ng/L. If is the SERS intensity at 1620 cm–1 when the concentration varies from 1000 ng/L to 5 pg/L. (D) Plot shows how the SERS intensity at 1230 cm–1 for amide-III band from tetracycline antibiotics varies with the concentration (ng/L). I0is the SERS intensity at 1230 cm–1 when the concentration is 1000 ng/L. If is the SERS intensity at 1230 cm–1 when the concentration varies from 1000 ng/L to 5 pg/L. (E) Tetracycline and moxifloxacin antibiotic removal efficiency from drinking water using theFGO-PEI based nanoplatform. For this experiment, we used 1000 ng/L of antibiotic infected drinking water. (F) Tetracycline and moxifloxacin antibiotic removal efficiency from drinking water using the GO-PEI based nanoplatform. For this experiment, we used 1000 ng/L of each antibiotic separately. (G) Tetracycline and moxifloxacin antibiotic removal efficiency from drinking water using the FGO based nanoplatform. For this experiment, we used 1000 ng/L of antibiotic infected drinking water. (H) Variation of moxifloxacin antibiotic removal efficiency with time for the FGO and FGO-PEI based nanoplatform. (I) Plot shows the variation of 1/qe with 1/Ce for moxifloxacin antibiotics using the PEI-FGO adsorber, where qe is the quantity of moxifloxacin antibiotics absorbed at equilibrium and Ce is the concentration of moxifloxacin antibiotics. (J) Moxifloxacin antibiotic removal efficiency from tap water, Mississippi river water, lake water, and drinking water using the FGO-PEI based nanoplatform. For this experiment, we used 1000 ng/L of moxifloxacin antibiotic infected water samples. (K) Tetracycline antibiotic removal efficiency from tap water, Mississippi river water, lake water, and drinking water using the FGO-PEI based nanoplatform. For this experiment, we used 1000 ng/L of tetracycline antibiotic infected water samples. (L) Removal efficiency of PFNA, PFBS, tetracycline, and moxifloxacin antibiotics simultaneously from tap water, Mississippi river water, lake water, and drinking water using the FGO-PEI based nanoplatform. For this experiment, we used 250 ng/L of perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS), 250 ng/L of PFNA, 250 ng/L of tetracycline, and 250 ng/L of moxifloxacin antibiotic infected water samples.