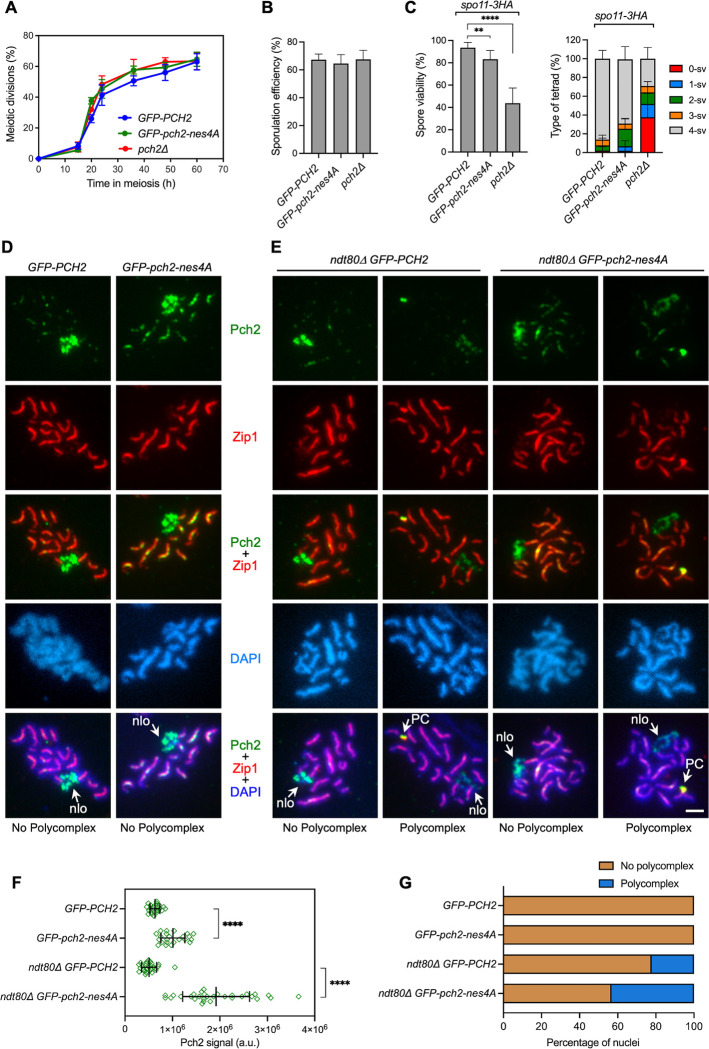
Fig 5. The pch2-nes4A mutant has little impact on an unperturbed ZIP1 meiosis.
(A) Time course analysis of meiotic nuclear divisions; the percentage of cells containing two or more nuclei is represented. Error bars: SD; n = 3. At least 300 cells were scored for each strain at every time point. (B) Sporulation efficiency, assessed by microscopic counting of asci, was examined after 3 days on sporulation plates. Error bars, SD; n = 3. At least 600 cells were counted for each strain. (C) Spore viability, assessed by tetrad dissection, is shown in the left graph. The percentage of tetrads containing 4-, 3-, 2-, 1-, and 0-viable spores is presented in the right graph. At least 144 tetrads were dissected for each strain. Error bars, SD. (D, E) Immunofluorescence of spread meiotic chromosomes at pachytene stained with anti-GFP antibodies (to detect GFP-Pch2; green) and anti-Zip1 antibodies (red), and DAPI (blue). Representative nuclei are shown. Spreads were prepared 15 h (D) or 24 h (E) after meiotic induction. Arrows point to the rDNA region (nlo) and polycomplex (PC). Scale bar, 2 μm. (F) Quantification of Pch2 signal on spread nuclei from the experiment shown in (D, E). a.u., arbitrary units. (G) Percentage of nuclei containing polycomplexes in the experiment shown in (D, E). Between 23 to 30 nuclei were scored in (F, G). Strains are: DP1023 (pch2Δ), DP1620 (GFP-PCH2), DP2052 (GFP-pch2-nes4A), DP1788 (spo11-3HA GFP-PCH2), DP2046 (spo11-3HA GFP-pch2-nes4A), DP1787 (spo11-3HA pch2Δ), DP1639 (ndt80Δ GFP-PCH2), and DP2053 (ndt80Δ GFP-pch2-nes4A).