Abstract
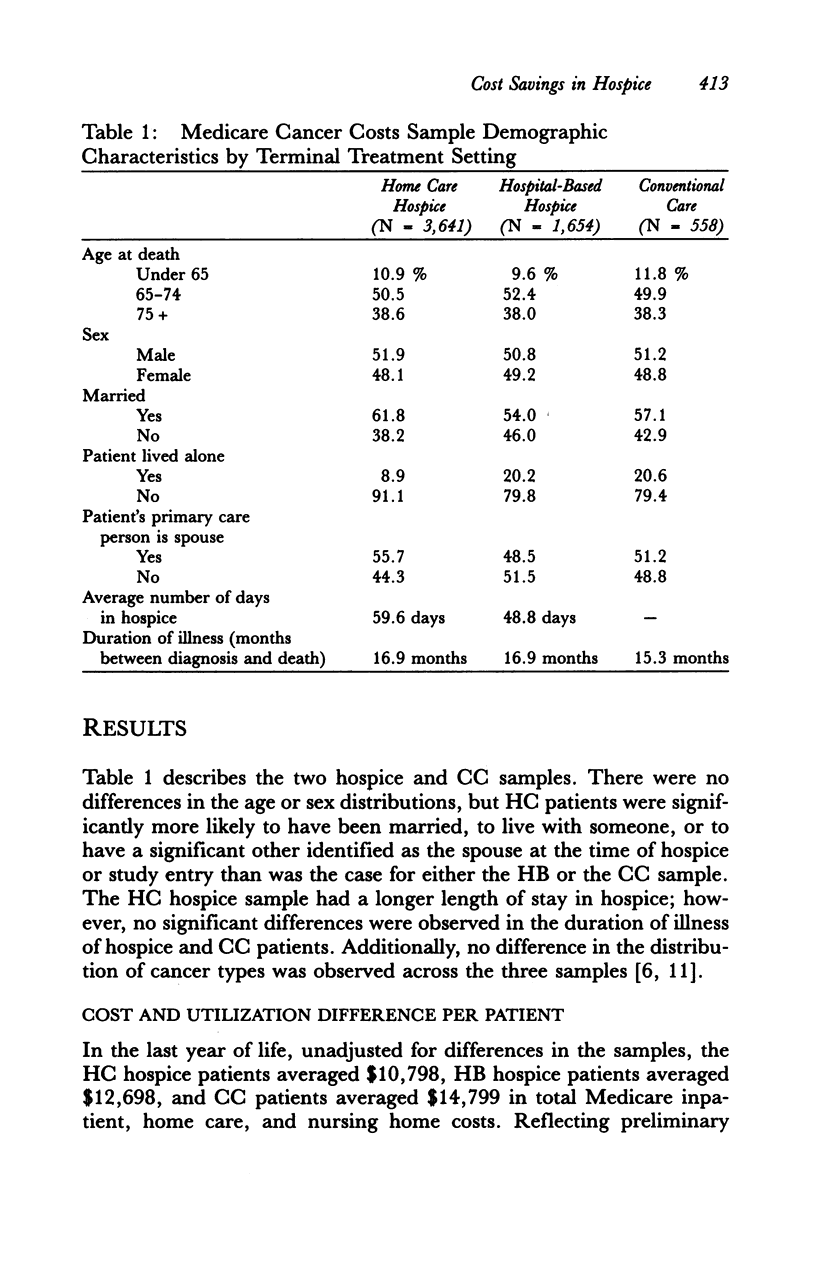
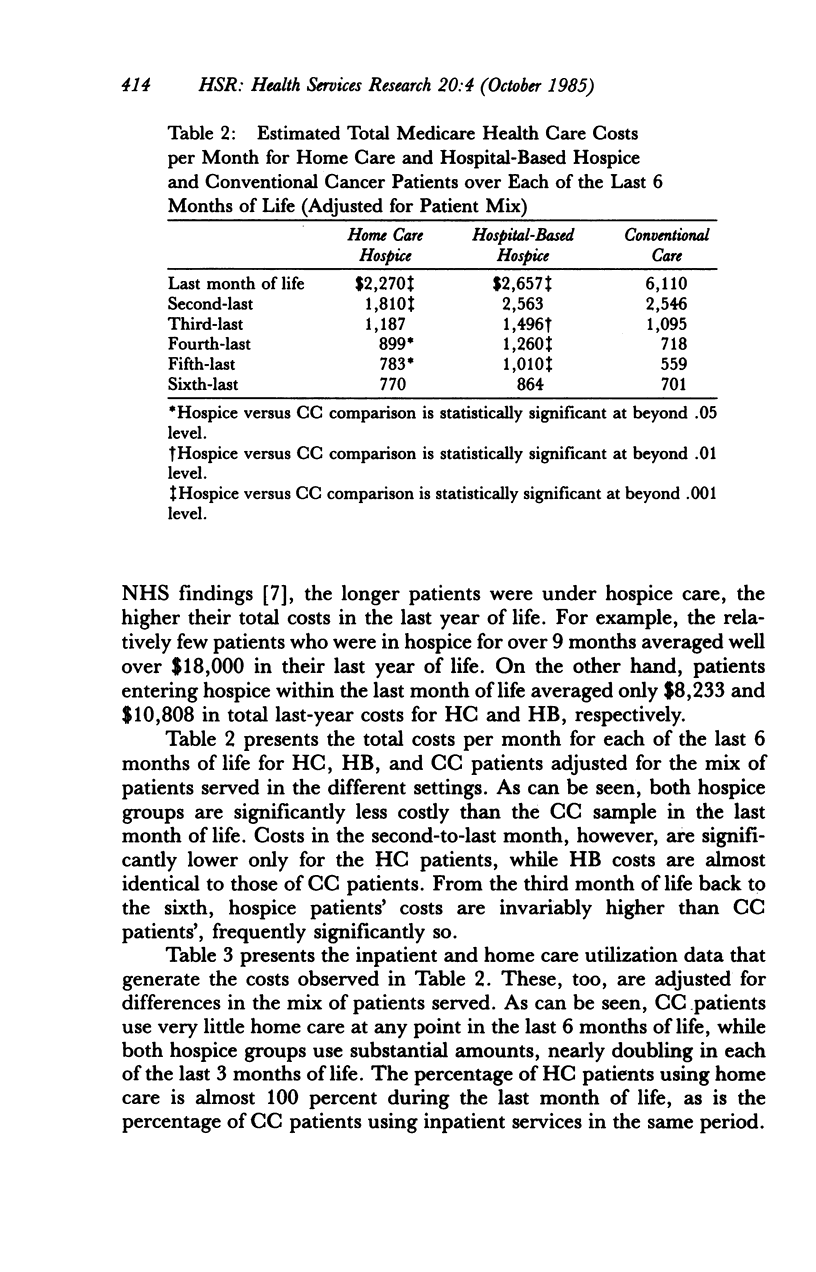
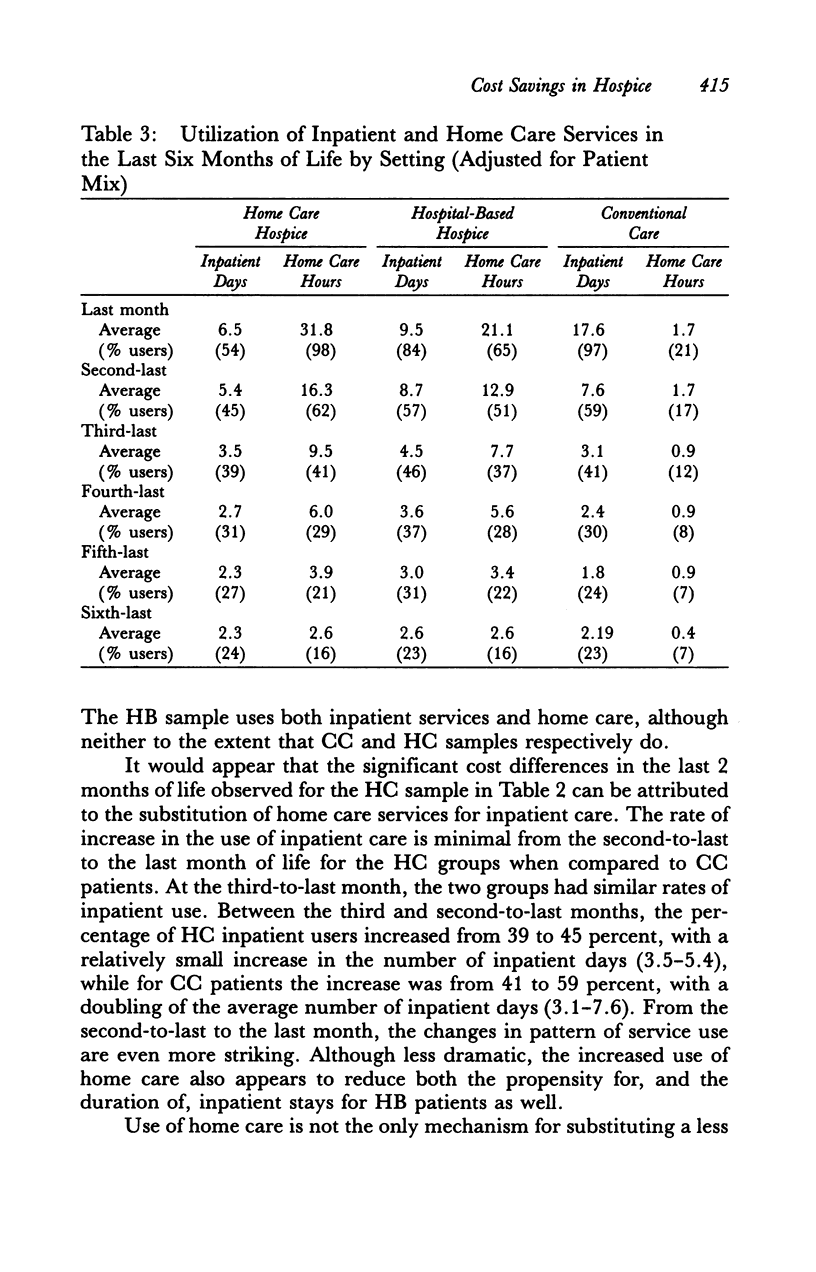
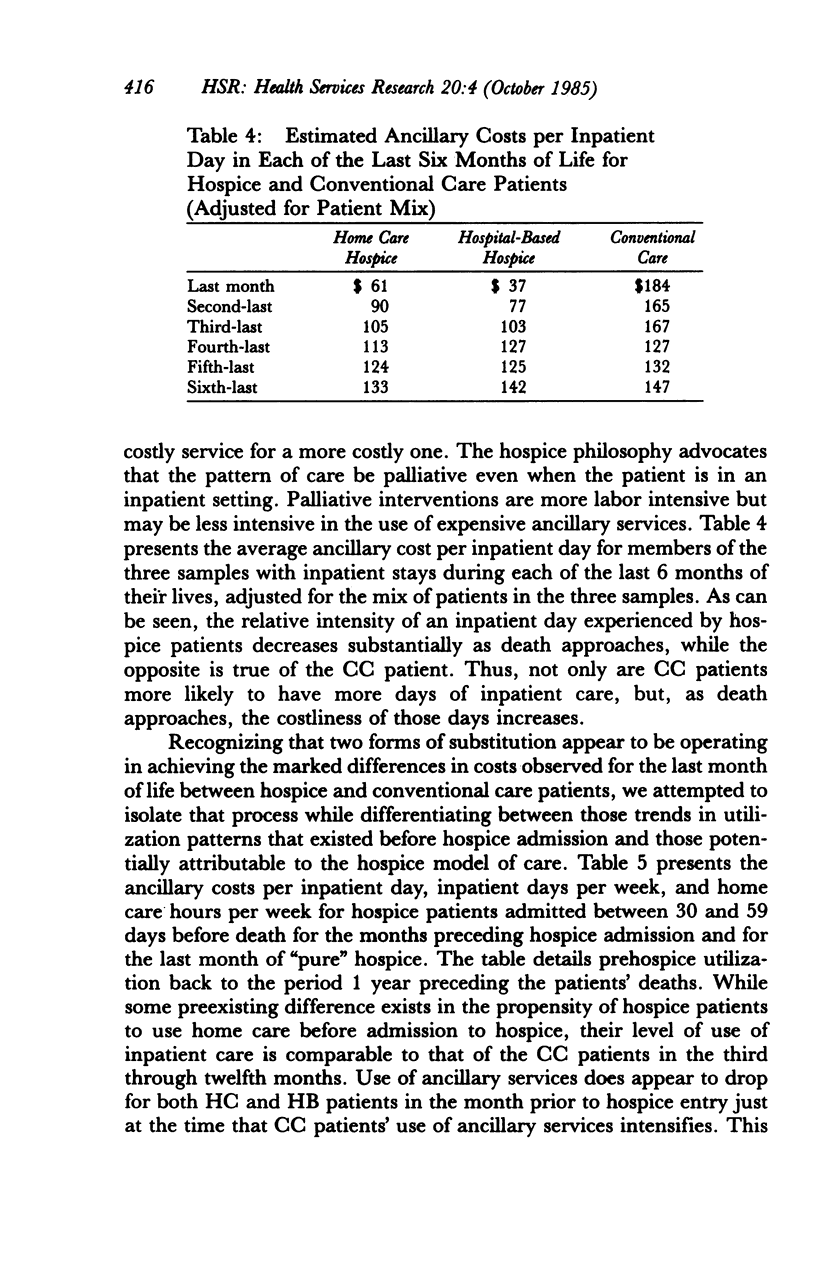
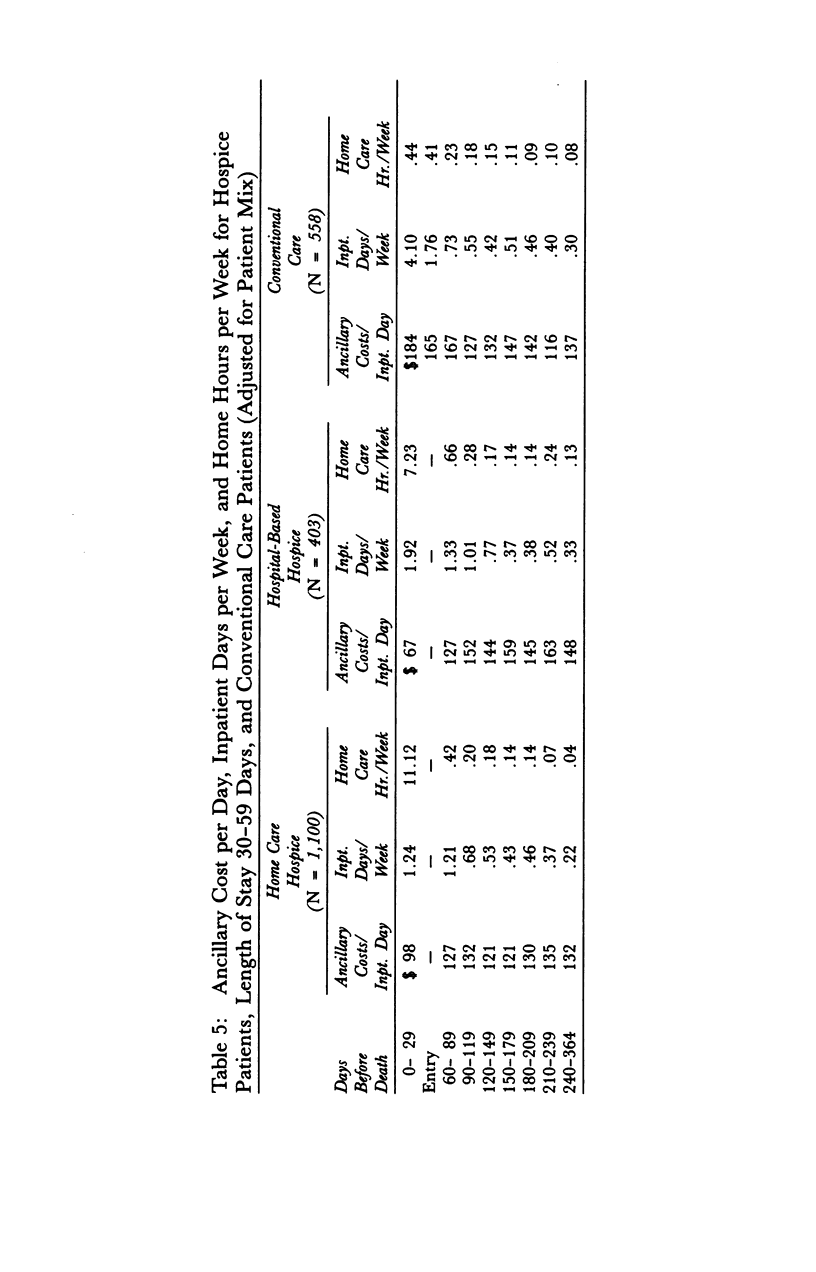
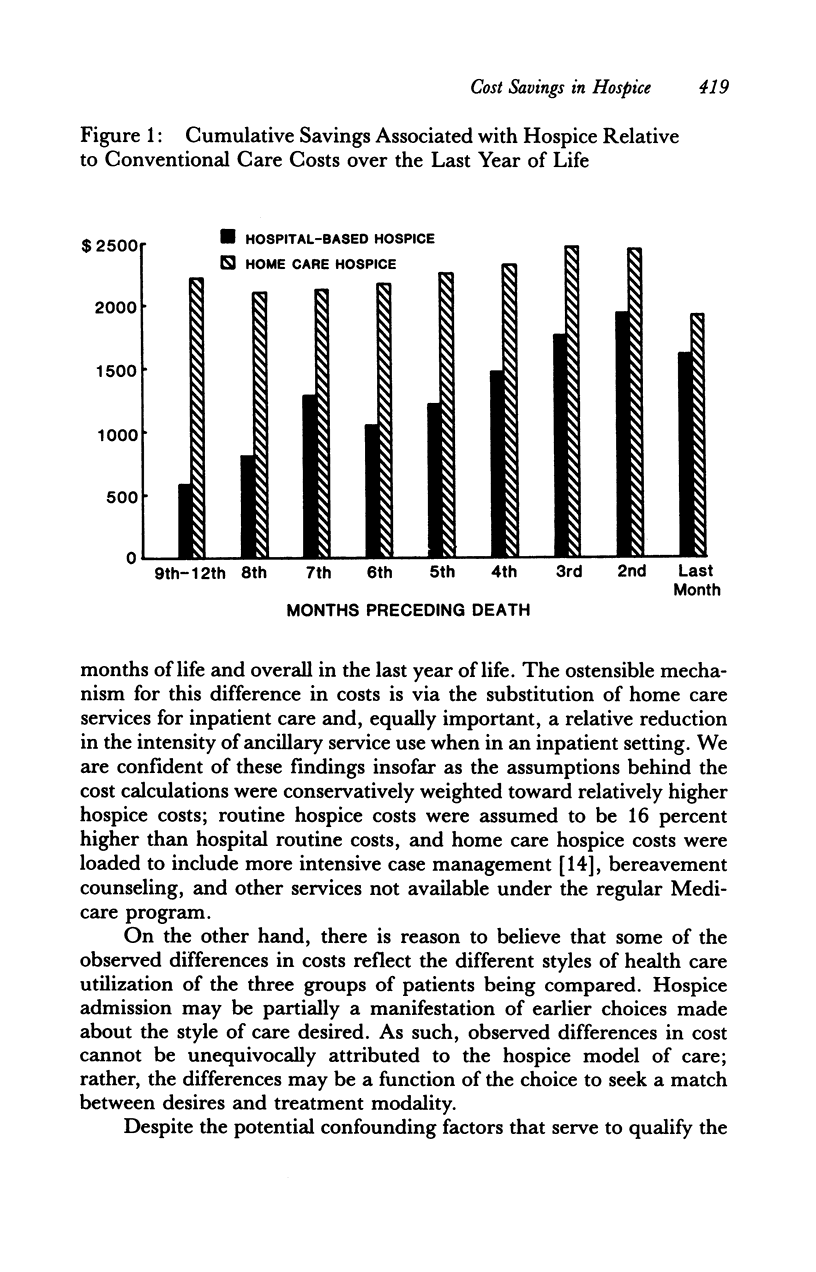
Medicare inpatient and home care costs over the last year of life of terminal cancer patients served in two types of hospices and in conventional care (CC) were compared as a part of the National Hospice Study (NHS). Both home care (HC) and hospital-based (HB) hospice patients had lower costs in the last month of life than did CC patients. HC patients substituted home care for inpatient care, yielding cost savings for lengths of hospice stay of up to 1 year. Although HB patients added home care to relatively high levels of inpatient care, their ancillary costs per inpatient day were significantly lower than those of CC patients. Thus, HB costs over the last year of life were also somewhat less than those of CC. The size of the savings associated with hospice care is sensitive to the type of hospice and the length of stay distribution of patients served; patients served longer have significantly higher costs in the last year of life.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amado A., Cronk B. A., Mileo R. Cost of terminal care: home hospice vs hospital. Nurs Outlook. 1979 Aug;27(8):522–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum H. G., Kidder D. What does hospice cost? Am J Public Health. 1984 Jul;74(7):689–697. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.7.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham R. W., Lupu D. A comparative study of hospice services in the United States. Am J Public Health. 1982 May;72(5):455–463. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.5.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkler S. A. The distinction between cost and charges. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):102–109. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer D. S., Mor V., Sherwood S., Morris J. N., Birnbaum H. National hospice study analysis plan. J Chronic Dis. 1983;36(11):737–780. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(83)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. H., Gibbs J. O., Crozier J. P., Cooper D. I., Jr, Newman J. F., Jr, Larsen A. M. Medical expenditures of terminal cancer patients during the last year of life. Inquiry. 1984 Winter;21(4):315–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor V., Birnbaum H. Medicare legislation for hospice care: implications of national hospice study data. Health Aff (Millwood) 1983 Summer;2(2):80–90. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2.2.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector W. D., Mor V. Utilization and charges for terminal cancer patients in Rhode Island. Inquiry. 1984 Winter;21(4):328–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


