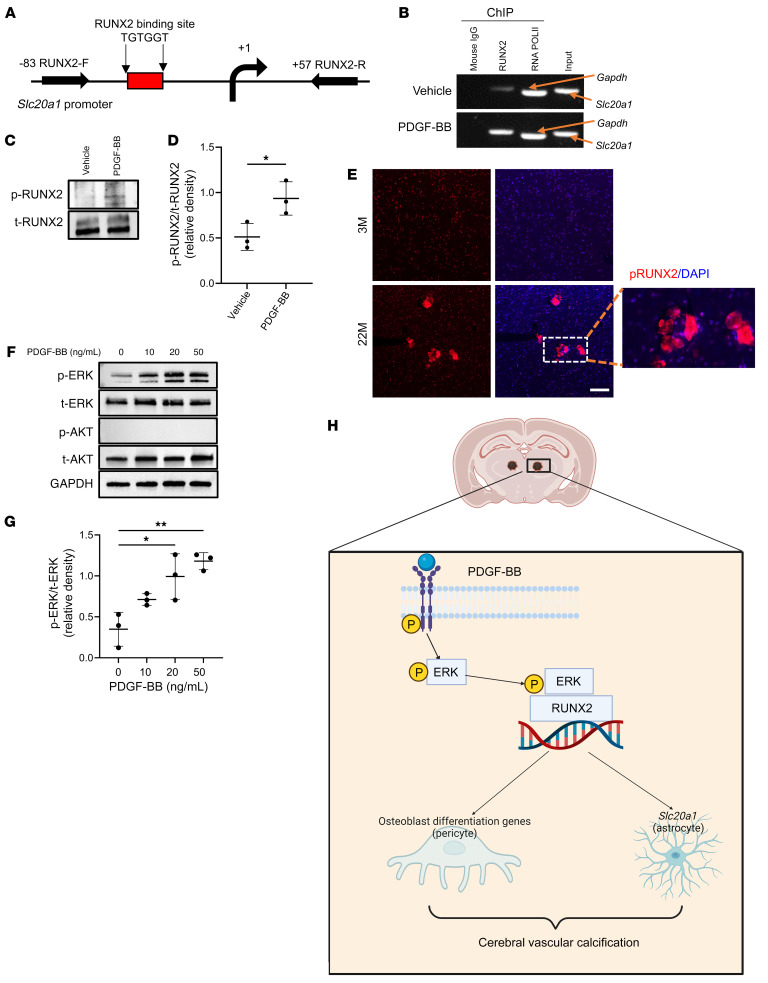
Figure 8. PDGF-BB activates Slc20a1 gene transcription through ERK/RUNX2 signaling.
(A) Schematic representation of the Slc20a1 promoter region. The location of the consensus RUNX2 binding site (TGTGGT) and the regions chosen for PCR amplification by the primers in the ChIP-qPCR assays are indicated. (B) Cerebral microvessels isolated from brain were treated with 20 ng/mL PDGF-BB or vehicle. Chromating DNA was immunoprecipitated using a specific antibody against RUNX2 or mouse IgG (negative control). DNA fragments were amplified with primers specific for the Slc20a1 promoter. As a positive control, an antibody against RNA polymerase II (RNA PolII) was used for immunoprecipitation, and primers specific for GAPDH were used for PCR. (C) Cerebral microvessels isolated from brain were treated with 20 ng/mL PDGF-BB or vehicle. Western blot analysis of p-RUNX2 and total RUNX2 (t-RUNX2). n = 3. (D) The relative density of p-RUNX2 to t-RUNX2 was calculated using ImageJ. n = 3. (E) Immunofluorescence staining of frozen brain tissue sections from 3- and 22-month-old male mice using antibodies against RUNX2. n = 3. Scale bar: 100 μm. Magnification ×10. (F) Cerebral microvessels isolated from brain were treated with increasing concentrations of PDGF-BB. Western blot analysis of p-ERK and p-AKT. n = 3. (G) Relative densities of p-ERK and t-ERK were calculated using ImageJ (n = 3). (H) Schematic model showing the molecular mechanisms underlying PDGF-BB–induced brain vascular calcification. All data are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, by ordinary 1-way ANOVA for multiple-group comparisons (G). *P < 0.05, by unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test for 2-group comparisons (D).